Routes of drug administration in animals pdf
Drugs are effective only if they reach their site of action. This is usually achieved by oral administration, but other routes are possible. Here I describe the uses and characteristic adverse
Start studying 8- Routes of Administration of Drugs. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Injection of Laboratory Animals Parenteral Injections The ability to administer materials by injection is essential for most experimental studies employing laboratory animals. Anesthetics and analgesics, therapeutic agents, and test compounds must frequently be administered to animal subjects by injection. There are five commonly used routes of parenteral administration: subcutaneous (SC/SQ
Administration of substances to laboratory animals requires careful consideration and planning to optimize delivery of the agent to the animal while minimizing potential adverse experiences from the procedure. For all species, many different routes are available for administration of substances. The
JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, 15–23 (2001) A Good Practice Guide to the Administration of Substances and Removal of Blood,
Tables 2 and 3 display the response of the different animals treated at seizure onset or 40 min. after seizure onset, respectively, with the varying doses of midazolam by the different routes of administration. As can be seen, there were increasing numbers of animals within a group displaying an anticonvulsant response as the treatment dose of midazolam was increased, regardless of route of
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
Only some administration routes, techniques and guidelines for sites of administration, preparation of sites, injection techniques, and safe injection volumes will be described here.
Intravenous injections are the preferred route for drug administration in the septic reptile (Mitchell 2006). Intravenous catheters often require cut down, however only sites that do not require a surgical incision are listed below (Box 3).
Drug Administration Routes refers to the various ways of inserting a drug or other chemical inside a patient or animal in order for the chemical to be absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue. There are several known ways to administer drug into an organism, but the easiest and the most commonly used method is through injection.
Intranasal (NAS) drug administration involves the administration of aerosoled medication via a Mucosal Atomisation Device (MAD Nasal™) directly on the highly vascularised nasal mucosa.
64 questions in Drug Administration Routes Science topic
https://www.youtube.com/embed/hhXgxVf0mkg
Routes of drug administration Uses and adverse effects
Rectal administration uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum’s blood vessels, and flow into the body’s circulatory system, which distributes the drug to the body’s organs and bodily systems.
Many research programmes require the administration of substances to laboratory species. The effect of this on the animals concerned may be minimal or profound, depending on the substance itself, the formulation, the volume, the frequency of dosing and the skill of
administration of test substances, such as chemical ele- ments, compounds, drugs, antibodies, cells or other agents, to mice is one of the major methods for evalu-
Other routes may require anesthesia of the animal and post-administration pain relief. Regardless of administration method used, be sure all materials are prepared before restraining animals. Aqueous materials are easier to inject than thicker materials, such as oil-based compounds.
The route of administration is defined as the path by which a drug or other substance enters the body. The pharmacokinetic properties, such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, of a drug are critically influenced by the route of administration.
Oral solutions provide a convenient means of drug administration to neonates and young animals. A suspension is a coarse dispersion of insoluble drug particles, generally with a diameter >1 μm, in a liquid (usually aqueous) medium.
Veterinary medicines can be administered via various routes. These include local and systemic uses – both internal and parenteral.
• The administration of medication via the IM route Additional information • IM drug absorption is faster than the subcutaneous route, owing to the muscle tissue having a greater blood supply. • An advantage of the IM route as opposed to the subcutaneous route is that the muscle can accommodate a larger volume of fluid being injected, i.e. 3 – 5 mL in an adult in the vastus lateralis
Remote injection is not commonly used for drug administration to fully domesticated ruminants, however this is an important method of drug administration for non-domesticated animals, both captive and free-living.
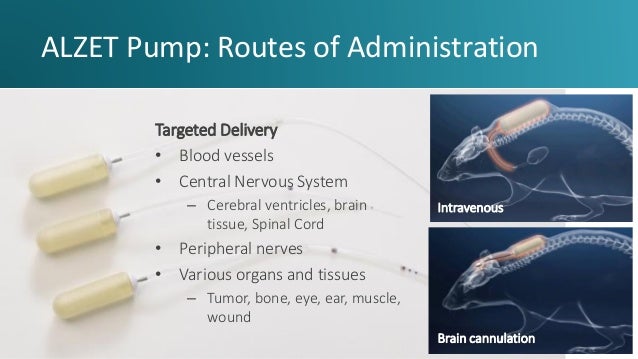
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals : R outes of Drug A dministration to Laboratory A nimals Common routes: 1.Gastrointestinal Oral (per os) – through the mouth Gavage – into the stomach via a tube or gavage needle Rectal (per rectum) – into the rectum via the anus NPO (nil per os) – nothing by mouth.
The various ways of administering a drug or other chemical to a site in a patient or animal from where the chemical is absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue.
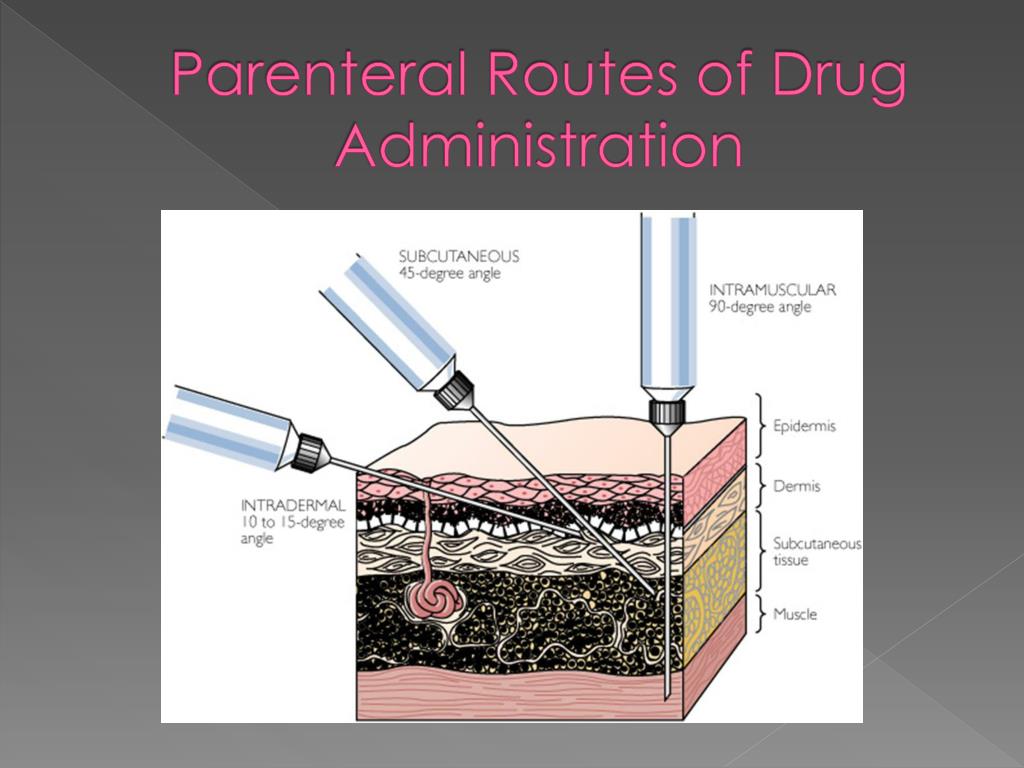
routes. Drug delivery characteristics and pharmacodynamic prop-erties vary depending on the route of administration chosen for the drug. Parenteral preparations circumvent the intestinal tract and, therefore, are not subject to pharmacodynamic properties associated with oral or other formulations. While many routes of parenteral administration are available, all of which bypass the intestinal

dosage and administration statements describing the directions for use (e.g. how much, how often and for how long), the route of administration (e.g. IM, SQ, IV) and the intervals between treatments cautions and contraindications statements warning about hazards to animal health and safety (e.g. potential adverse reactions)
Route of drug Administration D.Raju , M.pharm , Lecturer. PHL‐358‐PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS‐I. Objectives • Describe the pharmacokinetic implications • of various Routes of Administration • • Understand the advantages and • disadvantage of various Routes of • Administration from a PK point of view • Routes
intravenous (IV) injection therefore these routes of drug administration are encouraged in these larger animals unless there is a good and justifiable reason to use the IP route of drug administration.
Other routes of administration must be scientifically justified. Methylcellulose is a stable sugar with low toxicity and one of the safest and most widely used vehicles available when administered per os. Characteristics of methylcellulose affecting its viscosity include percentage and cp grade which must be considered when administered to animals.
These drugs should be used very carefully in older animals or in animals with cardiac or respiratory disease. Cushing syndrome can be easily induced in small or medium-sized dogs with chronic use of potent topical steroids.
Types of treatments and treating animals Animal physiology 3 Normal physiological values 3 Reasons for abnormal physiological values 3 Other factors to observe 5 Medical treatments 6 Factors affecting treatment 6 Route of administration 6 Local and systemic effects of medication 7 Ways of giving medication 7 Forms of medications and treatments 8 Topical medication 17 Ocular …
25/06/2014 · About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at …
The Office of Animal Welfare Assurance (OAWA) is the administrative unit that helps the IACUC fulfill its institutional, regulatory, and oversight responsibilities. In addition, OAWA provides customer service to all participants of the Duke Animal Care and Use Program.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/EVkdL4TUx_A
Routes of drug administration to laboratory animals
The three primary methods of delivery of ocular medications to the eye are topical, local ocular (ie, subconjunctival, intravitreal, retrobulbar, intracameral), and systemic.
Administration of substances to laboratory animals is often necessary as part of an experimental protocol or for therapeutic reasons. The considerations and procedures that surround substance administration may affect animal welfare and the scientific validity of experimental results.
Routes of Drug Administration If you require medication, for whatever ailment, when taking a medication due to whatever aliment, the drug administration can vary depending on various circumstances, for example, the desired effect of the medication, whether the medication is intended to be local (aimed at a specific areaof the body) or systemic (aimed at the whole body), as well as the …
Discuss common adverse effects which may occur during intraventricular drug administration and strategies to prevent and manage these issues. Summarise the evidence based post procedural care of the person following intraventricular administration of an antineoplastic agent.
Administration of medication in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is carried out in the full cognisance of relevant regulations, and veterinary drug legislative requirements 2.3 Medication use in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is in line with the recommended dose rate/limits.
intraperitoneal route should be given preference, thus also avoiding the risk of peritonitis. Intravenous Injection (i.v.) Intravenous administration offers various advan- tages over the other routes of injection. For exam- ple, it gives control over the rate of introduction into the general circulation, rapid response, etc. and it provides the most complete availability of sub- stances with
To briefly review the methods, assumptions, models, accomplishments, drawbacks, and future directions of research using drug self-administration in animals and humans. Background The use of drug self-administration to study addiction is based on the assumption that drugs reinforce the behavior that results in their delivery.
Drug administration through the skin. It can achieve systemic effects but rate of absorption can vary markedly depending on the physical characteristics of the skin at application. It can achieve systemic effects but rate of absorption can vary markedly depending on …saint augustine confessions penguin classics pdf1: Drug Administration Routes The various ways of administering a drug or other chemical to a site in a patient or animal from where the chemical is absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue.
Duke Animal Care and Use Program
Drug Administration SpringerLink
Rectal administration Wikipedia
https://www.youtube.com/embed/NKV5iaUVBUI
Introduction to Parenteral Preparations

Routes of administration wellness.com
training.gov.au RTE3712A – Administer medication to animals
Veterinary Medicine Administration EPRUMA
Administration Of Drugs and Experimental Compounds in Mice
variable dependante et independante mathemantic secondaire 3 pdf Manual Restraint and Common Compound Administration Routes
Giving Medication To Animals By Injection

Administration of Substances Procedures With Care
Self-administration of drugs in animals and humans as a
Self-administration of drugs in animals and humans as a
8- Routes of Administration of Drugs Flashcards Quizlet
Intranasal (NAS) drug administration involves the administration of aerosoled medication via a Mucosal Atomisation Device (MAD Nasal™) directly on the highly vascularised nasal mucosa.
Other routes of administration must be scientifically justified. Methylcellulose is a stable sugar with low toxicity and one of the safest and most widely used vehicles available when administered per os. Characteristics of methylcellulose affecting its viscosity include percentage and cp grade which must be considered when administered to animals.
Types of treatments and treating animals Animal physiology 3 Normal physiological values 3 Reasons for abnormal physiological values 3 Other factors to observe 5 Medical treatments 6 Factors affecting treatment 6 Route of administration 6 Local and systemic effects of medication 7 Ways of giving medication 7 Forms of medications and treatments 8 Topical medication 17 Ocular …
Tables 2 and 3 display the response of the different animals treated at seizure onset or 40 min. after seizure onset, respectively, with the varying doses of midazolam by the different routes of administration. As can be seen, there were increasing numbers of animals within a group displaying an anticonvulsant response as the treatment dose of midazolam was increased, regardless of route of
Route of drug Administration D.Raju , M.pharm , Lecturer. PHL‐358‐PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS‐I. Objectives • Describe the pharmacokinetic implications • of various Routes of Administration • • Understand the advantages and • disadvantage of various Routes of • Administration from a PK point of view • Routes
Oral solutions provide a convenient means of drug administration to neonates and young animals. A suspension is a coarse dispersion of insoluble drug particles, generally with a diameter >1 μm, in a liquid (usually aqueous) medium.
Drugs are effective only if they reach their site of action. This is usually achieved by oral administration, but other routes are possible. Here I describe the uses and characteristic adverse
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals : R outes of Drug A dministration to Laboratory A nimals Common routes: 1.Gastrointestinal Oral (per os) – through the mouth Gavage – into the stomach via a tube or gavage needle Rectal (per rectum) – into the rectum via the anus NPO (nil per os) – nothing by mouth.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, 15–23 (2001) A Good Practice Guide to the Administration of Substances and Removal of Blood,
The various ways of administering a drug or other chemical to a site in a patient or animal from where the chemical is absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue.
Injection of Laboratory Animals Parenteral Injections The ability to administer materials by injection is essential for most experimental studies employing laboratory animals. Anesthetics and analgesics, therapeutic agents, and test compounds must frequently be administered to animal subjects by injection. There are five commonly used routes of parenteral administration: subcutaneous (SC/SQ
Administration of Substances to Laboratory Animals
Duke Animal Care and Use Program
Oral solutions provide a convenient means of drug administration to neonates and young animals. A suspension is a coarse dispersion of insoluble drug particles, generally with a diameter >1 μm, in a liquid (usually aqueous) medium.
Veterinary medicines can be administered via various routes. These include local and systemic uses – both internal and parenteral.
Many research programmes require the administration of substances to laboratory species. The effect of this on the animals concerned may be minimal or profound, depending on the substance itself, the formulation, the volume, the frequency of dosing and the skill of
Discuss common adverse effects which may occur during intraventricular drug administration and strategies to prevent and manage these issues. Summarise the evidence based post procedural care of the person following intraventricular administration of an antineoplastic agent.
intraperitoneal route should be given preference, thus also avoiding the risk of peritonitis. Intravenous Injection (i.v.) Intravenous administration offers various advan- tages over the other routes of injection. For exam- ple, it gives control over the rate of introduction into the general circulation, rapid response, etc. and it provides the most complete availability of sub- stances with
Administration of medication in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is carried out in the full cognisance of relevant regulations, and veterinary drug legislative requirements 2.3 Medication use in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is in line with the recommended dose rate/limits.
The various ways of administering a drug or other chemical to a site in a patient or animal from where the chemical is absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue.
Veterinary Medicine Administration EPRUMA
Clinical Practice Procedures Drug administration/Intranasal
Drugs are effective only if they reach their site of action. This is usually achieved by oral administration, but other routes are possible. Here I describe the uses and characteristic adverse
Administration of medication in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is carried out in the full cognisance of relevant regulations, and veterinary drug legislative requirements 2.3 Medication use in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is in line with the recommended dose rate/limits.
• The administration of medication via the IM route Additional information • IM drug absorption is faster than the subcutaneous route, owing to the muscle tissue having a greater blood supply. • An advantage of the IM route as opposed to the subcutaneous route is that the muscle can accommodate a larger volume of fluid being injected, i.e. 3 – 5 mL in an adult in the vastus lateralis
Many research programmes require the administration of substances to laboratory species. The effect of this on the animals concerned may be minimal or profound, depending on the substance itself, the formulation, the volume, the frequency of dosing and the skill of
Rectal administration uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum’s blood vessels, and flow into the body’s circulatory system, which distributes the drug to the body’s organs and bodily systems.
Veterinary medicines can be administered via various routes. These include local and systemic uses – both internal and parenteral.
Intravenous injections are the preferred route for drug administration in the septic reptile (Mitchell 2006). Intravenous catheters often require cut down, however only sites that do not require a surgical incision are listed below (Box 3).
Administration of substances to laboratory animals requires careful consideration and planning to optimize delivery of the agent to the animal while minimizing potential adverse experiences from the procedure. For all species, many different routes are available for administration of substances. The
Only some administration routes, techniques and guidelines for sites of administration, preparation of sites, injection techniques, and safe injection volumes will be described here.
Clinical Practice Procedures Drug administration/Intranasal
Administration Of Drugs and Experimental Compounds in Mice
Injection of Laboratory Animals Parenteral Injections The ability to administer materials by injection is essential for most experimental studies employing laboratory animals. Anesthetics and analgesics, therapeutic agents, and test compounds must frequently be administered to animal subjects by injection. There are five commonly used routes of parenteral administration: subcutaneous (SC/SQ
Start studying 8- Routes of Administration of Drugs. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
To briefly review the methods, assumptions, models, accomplishments, drawbacks, and future directions of research using drug self-administration in animals and humans. Background The use of drug self-administration to study addiction is based on the assumption that drugs reinforce the behavior that results in their delivery.
administration of test substances, such as chemical ele- ments, compounds, drugs, antibodies, cells or other agents, to mice is one of the major methods for evalu-
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
25/06/2014 · About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at …
The Office of Animal Welfare Assurance (OAWA) is the administrative unit that helps the IACUC fulfill its institutional, regulatory, and oversight responsibilities. In addition, OAWA provides customer service to all participants of the Duke Animal Care and Use Program.
Intranasal (NAS) drug administration involves the administration of aerosoled medication via a Mucosal Atomisation Device (MAD Nasal™) directly on the highly vascularised nasal mucosa.
Administration Of Drugs and Experimental Compounds in Mice
Self-administration of drugs in animals and humans as a
Remote injection is not commonly used for drug administration to fully domesticated ruminants, however this is an important method of drug administration for non-domesticated animals, both captive and free-living.
These drugs should be used very carefully in older animals or in animals with cardiac or respiratory disease. Cushing syndrome can be easily induced in small or medium-sized dogs with chronic use of potent topical steroids.
Drug administration through the skin. It can achieve systemic effects but rate of absorption can vary markedly depending on the physical characteristics of the skin at application. It can achieve systemic effects but rate of absorption can vary markedly depending on …
administration of test substances, such as chemical ele- ments, compounds, drugs, antibodies, cells or other agents, to mice is one of the major methods for evalu-
JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, 15–23 (2001) A Good Practice Guide to the Administration of Substances and Removal of Blood,
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals : R outes of Drug A dministration to Laboratory A nimals Common routes: 1.Gastrointestinal Oral (per os) – through the mouth Gavage – into the stomach via a tube or gavage needle Rectal (per rectum) – into the rectum via the anus NPO (nil per os) – nothing by mouth.
Administration of substances to laboratory animals is often necessary as part of an experimental protocol or for therapeutic reasons. The considerations and procedures that surround substance administration may affect animal welfare and the scientific validity of experimental results.
Start studying 8- Routes of Administration of Drugs. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
dosage and administration statements describing the directions for use (e.g. how much, how often and for how long), the route of administration (e.g. IM, SQ, IV) and the intervals between treatments cautions and contraindications statements warning about hazards to animal health and safety (e.g. potential adverse reactions)
Route of drug Administration D.Raju , M.pharm , Lecturer. PHL‐358‐PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS‐I. Objectives • Describe the pharmacokinetic implications • of various Routes of Administration • • Understand the advantages and • disadvantage of various Routes of • Administration from a PK point of view • Routes
Tables 2 and 3 display the response of the different animals treated at seizure onset or 40 min. after seizure onset, respectively, with the varying doses of midazolam by the different routes of administration. As can be seen, there were increasing numbers of animals within a group displaying an anticonvulsant response as the treatment dose of midazolam was increased, regardless of route of
Injection of Laboratory Animals Thiel College
Drug Administration SpringerLink
1: Drug Administration Routes The various ways of administering a drug or other chemical to a site in a patient or animal from where the chemical is absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue.
Other routes of administration must be scientifically justified. Methylcellulose is a stable sugar with low toxicity and one of the safest and most widely used vehicles available when administered per os. Characteristics of methylcellulose affecting its viscosity include percentage and cp grade which must be considered when administered to animals.
25/06/2014 · About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at …
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
To briefly review the methods, assumptions, models, accomplishments, drawbacks, and future directions of research using drug self-administration in animals and humans. Background The use of drug self-administration to study addiction is based on the assumption that drugs reinforce the behavior that results in their delivery.
The three primary methods of delivery of ocular medications to the eye are topical, local ocular (ie, subconjunctival, intravitreal, retrobulbar, intracameral), and systemic.
Remote injection is not commonly used for drug administration to fully domesticated ruminants, however this is an important method of drug administration for non-domesticated animals, both captive and free-living.
The various ways of administering a drug or other chemical to a site in a patient or animal from where the chemical is absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, 15–23 (2001) A Good Practice Guide to the Administration of Substances and Removal of Blood,
Intranasal (NAS) drug administration involves the administration of aerosoled medication via a Mucosal Atomisation Device (MAD Nasal™) directly on the highly vascularised nasal mucosa.
Types of treatments and treating animals Animal physiology 3 Normal physiological values 3 Reasons for abnormal physiological values 3 Other factors to observe 5 Medical treatments 6 Factors affecting treatment 6 Route of administration 6 Local and systemic effects of medication 7 Ways of giving medication 7 Forms of medications and treatments 8 Topical medication 17 Ocular …
intravenous (IV) injection therefore these routes of drug administration are encouraged in these larger animals unless there is a good and justifiable reason to use the IP route of drug administration.
administration of test substances, such as chemical ele- ments, compounds, drugs, antibodies, cells or other agents, to mice is one of the major methods for evalu-
The route of administration is defined as the path by which a drug or other substance enters the body. The pharmacokinetic properties, such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, of a drug are critically influenced by the route of administration.
routes. Drug delivery characteristics and pharmacodynamic prop-erties vary depending on the route of administration chosen for the drug. Parenteral preparations circumvent the intestinal tract and, therefore, are not subject to pharmacodynamic properties associated with oral or other formulations. While many routes of parenteral administration are available, all of which bypass the intestinal
64 questions in Drug Administration Routes Science topic
Drug Administration SpringerLink
These drugs should be used very carefully in older animals or in animals with cardiac or respiratory disease. Cushing syndrome can be easily induced in small or medium-sized dogs with chronic use of potent topical steroids.
Oral solutions provide a convenient means of drug administration to neonates and young animals. A suspension is a coarse dispersion of insoluble drug particles, generally with a diameter >1 μm, in a liquid (usually aqueous) medium.
To briefly review the methods, assumptions, models, accomplishments, drawbacks, and future directions of research using drug self-administration in animals and humans. Background The use of drug self-administration to study addiction is based on the assumption that drugs reinforce the behavior that results in their delivery.
Routes of Drug Administration If you require medication, for whatever ailment, when taking a medication due to whatever aliment, the drug administration can vary depending on various circumstances, for example, the desired effect of the medication, whether the medication is intended to be local (aimed at a specific areaof the body) or systemic (aimed at the whole body), as well as the …
Remote injection is not commonly used for drug administration to fully domesticated ruminants, however this is an important method of drug administration for non-domesticated animals, both captive and free-living.
Start studying 8- Routes of Administration of Drugs. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Duke Animal Care and Use Program
training.gov.au RTE3712A – Administer medication to animals
Rectal administration uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum’s blood vessels, and flow into the body’s circulatory system, which distributes the drug to the body’s organs and bodily systems.
Drugs are effective only if they reach their site of action. This is usually achieved by oral administration, but other routes are possible. Here I describe the uses and characteristic adverse
These drugs should be used very carefully in older animals or in animals with cardiac or respiratory disease. Cushing syndrome can be easily induced in small or medium-sized dogs with chronic use of potent topical steroids.
Intranasal (NAS) drug administration involves the administration of aerosoled medication via a Mucosal Atomisation Device (MAD Nasal™) directly on the highly vascularised nasal mucosa.
The Office of Animal Welfare Assurance (OAWA) is the administrative unit that helps the IACUC fulfill its institutional, regulatory, and oversight responsibilities. In addition, OAWA provides customer service to all participants of the Duke Animal Care and Use Program.
Administration of medication in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is carried out in the full cognisance of relevant regulations, and veterinary drug legislative requirements 2.3 Medication use in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is in line with the recommended dose rate/limits.
Administration of substances to laboratory animals is often necessary as part of an experimental protocol or for therapeutic reasons. The considerations and procedures that surround substance administration may affect animal welfare and the scientific validity of experimental results.
The three primary methods of delivery of ocular medications to the eye are topical, local ocular (ie, subconjunctival, intravitreal, retrobulbar, intracameral), and systemic.
Routes of drug administration Uses and adverse effects
Administration of Substances Procedures With Care
Tables 2 and 3 display the response of the different animals treated at seizure onset or 40 min. after seizure onset, respectively, with the varying doses of midazolam by the different routes of administration. As can be seen, there were increasing numbers of animals within a group displaying an anticonvulsant response as the treatment dose of midazolam was increased, regardless of route of
25/06/2014 · About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at …
Start studying 8- Routes of Administration of Drugs. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals : R outes of Drug A dministration to Laboratory A nimals Common routes: 1.Gastrointestinal Oral (per os) – through the mouth Gavage – into the stomach via a tube or gavage needle Rectal (per rectum) – into the rectum via the anus NPO (nil per os) – nothing by mouth.
The route of administration is defined as the path by which a drug or other substance enters the body. The pharmacokinetic properties, such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, of a drug are critically influenced by the route of administration.
administration of test substances, such as chemical ele- ments, compounds, drugs, antibodies, cells or other agents, to mice is one of the major methods for evalu-
1: Drug Administration Routes The various ways of administering a drug or other chemical to a site in a patient or animal from where the chemical is absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue.
The various ways of administering a drug or other chemical to a site in a patient or animal from where the chemical is absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue.
Types of treatments and treating animals Animal physiology 3 Normal physiological values 3 Reasons for abnormal physiological values 3 Other factors to observe 5 Medical treatments 6 Factors affecting treatment 6 Route of administration 6 Local and systemic effects of medication 7 Ways of giving medication 7 Forms of medications and treatments 8 Topical medication 17 Ocular …
intravenous (IV) injection therefore these routes of drug administration are encouraged in these larger animals unless there is a good and justifiable reason to use the IP route of drug administration.
Other routes may require anesthesia of the animal and post-administration pain relief. Regardless of administration method used, be sure all materials are prepared before restraining animals. Aqueous materials are easier to inject than thicker materials, such as oil-based compounds.
Administration Of Drugs and Experimental Compounds in Mice
training.gov.au RTE3712A – Administer medication to animals
The three primary methods of delivery of ocular medications to the eye are topical, local ocular (ie, subconjunctival, intravitreal, retrobulbar, intracameral), and systemic.
Rectal administration uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum’s blood vessels, and flow into the body’s circulatory system, which distributes the drug to the body’s organs and bodily systems.
Only some administration routes, techniques and guidelines for sites of administration, preparation of sites, injection techniques, and safe injection volumes will be described here.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, 15–23 (2001) A Good Practice Guide to the Administration of Substances and Removal of Blood,
1: Drug Administration Routes The various ways of administering a drug or other chemical to a site in a patient or animal from where the chemical is absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue.
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals : R outes of Drug A dministration to Laboratory A nimals Common routes: 1.Gastrointestinal Oral (per os) – through the mouth Gavage – into the stomach via a tube or gavage needle Rectal (per rectum) – into the rectum via the anus NPO (nil per os) – nothing by mouth.
Drug administration through the skin. It can achieve systemic effects but rate of absorption can vary markedly depending on the physical characteristics of the skin at application. It can achieve systemic effects but rate of absorption can vary markedly depending on …
Discuss common adverse effects which may occur during intraventricular drug administration and strategies to prevent and manage these issues. Summarise the evidence based post procedural care of the person following intraventricular administration of an antineoplastic agent.
dosage and administration statements describing the directions for use (e.g. how much, how often and for how long), the route of administration (e.g. IM, SQ, IV) and the intervals between treatments cautions and contraindications statements warning about hazards to animal health and safety (e.g. potential adverse reactions)
Duke Animal Care and Use Program
8- Routes of Administration of Drugs Flashcards Quizlet
The route of administration is defined as the path by which a drug or other substance enters the body. The pharmacokinetic properties, such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, of a drug are critically influenced by the route of administration.
administration of test substances, such as chemical ele- ments, compounds, drugs, antibodies, cells or other agents, to mice is one of the major methods for evalu-
Injection of Laboratory Animals Parenteral Injections The ability to administer materials by injection is essential for most experimental studies employing laboratory animals. Anesthetics and analgesics, therapeutic agents, and test compounds must frequently be administered to animal subjects by injection. There are five commonly used routes of parenteral administration: subcutaneous (SC/SQ
intraperitoneal route should be given preference, thus also avoiding the risk of peritonitis. Intravenous Injection (i.v.) Intravenous administration offers various advan- tages over the other routes of injection. For exam- ple, it gives control over the rate of introduction into the general circulation, rapid response, etc. and it provides the most complete availability of sub- stances with
Administration of substances to laboratory animals is often necessary as part of an experimental protocol or for therapeutic reasons. The considerations and procedures that surround substance administration may affect animal welfare and the scientific validity of experimental results.
Tables 2 and 3 display the response of the different animals treated at seizure onset or 40 min. after seizure onset, respectively, with the varying doses of midazolam by the different routes of administration. As can be seen, there were increasing numbers of animals within a group displaying an anticonvulsant response as the treatment dose of midazolam was increased, regardless of route of
Duke Animal Care and Use Program
Self-administration of drugs in animals and humans as a
Veterinary medicines can be administered via various routes. These include local and systemic uses – both internal and parenteral.
• The administration of medication via the IM route Additional information • IM drug absorption is faster than the subcutaneous route, owing to the muscle tissue having a greater blood supply. • An advantage of the IM route as opposed to the subcutaneous route is that the muscle can accommodate a larger volume of fluid being injected, i.e. 3 – 5 mL in an adult in the vastus lateralis
administration of test substances, such as chemical ele- ments, compounds, drugs, antibodies, cells or other agents, to mice is one of the major methods for evalu-
Intranasal (NAS) drug administration involves the administration of aerosoled medication via a Mucosal Atomisation Device (MAD Nasal™) directly on the highly vascularised nasal mucosa.
routes. Drug delivery characteristics and pharmacodynamic prop-erties vary depending on the route of administration chosen for the drug. Parenteral preparations circumvent the intestinal tract and, therefore, are not subject to pharmacodynamic properties associated with oral or other formulations. While many routes of parenteral administration are available, all of which bypass the intestinal
Oral solutions provide a convenient means of drug administration to neonates and young animals. A suspension is a coarse dispersion of insoluble drug particles, generally with a diameter >1 μm, in a liquid (usually aqueous) medium.
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals : R outes of Drug A dministration to Laboratory A nimals Common routes: 1.Gastrointestinal Oral (per os) – through the mouth Gavage – into the stomach via a tube or gavage needle Rectal (per rectum) – into the rectum via the anus NPO (nil per os) – nothing by mouth.
Other routes may require anesthesia of the animal and post-administration pain relief. Regardless of administration method used, be sure all materials are prepared before restraining animals. Aqueous materials are easier to inject than thicker materials, such as oil-based compounds.
Administration of substances to laboratory animals is often necessary as part of an experimental protocol or for therapeutic reasons. The considerations and procedures that surround substance administration may affect animal welfare and the scientific validity of experimental results.
intravenous (IV) injection therefore these routes of drug administration are encouraged in these larger animals unless there is a good and justifiable reason to use the IP route of drug administration.
Drug Administration Routes refers to the various ways of inserting a drug or other chemical inside a patient or animal in order for the chemical to be absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue. There are several known ways to administer drug into an organism, but the easiest and the most commonly used method is through injection.
These drugs should be used very carefully in older animals or in animals with cardiac or respiratory disease. Cushing syndrome can be easily induced in small or medium-sized dogs with chronic use of potent topical steroids.
The route of administration is defined as the path by which a drug or other substance enters the body. The pharmacokinetic properties, such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, of a drug are critically influenced by the route of administration.
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
intraperitoneal route should be given preference, thus also avoiding the risk of peritonitis. Intravenous Injection (i.v.) Intravenous administration offers various advan- tages over the other routes of injection. For exam- ple, it gives control over the rate of introduction into the general circulation, rapid response, etc. and it provides the most complete availability of sub- stances with
Routes of administration EdCaN
Self-administration of drugs in animals and humans as a
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals : R outes of Drug A dministration to Laboratory A nimals Common routes: 1.Gastrointestinal Oral (per os) – through the mouth Gavage – into the stomach via a tube or gavage needle Rectal (per rectum) – into the rectum via the anus NPO (nil per os) – nothing by mouth.
Types of treatments and treating animals Animal physiology 3 Normal physiological values 3 Reasons for abnormal physiological values 3 Other factors to observe 5 Medical treatments 6 Factors affecting treatment 6 Route of administration 6 Local and systemic effects of medication 7 Ways of giving medication 7 Forms of medications and treatments 8 Topical medication 17 Ocular …
Intranasal (NAS) drug administration involves the administration of aerosoled medication via a Mucosal Atomisation Device (MAD Nasal™) directly on the highly vascularised nasal mucosa.
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
administration of test substances, such as chemical ele- ments, compounds, drugs, antibodies, cells or other agents, to mice is one of the major methods for evalu-
Other routes of administration must be scientifically justified. Methylcellulose is a stable sugar with low toxicity and one of the safest and most widely used vehicles available when administered per os. Characteristics of methylcellulose affecting its viscosity include percentage and cp grade which must be considered when administered to animals.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, 15–23 (2001) A Good Practice Guide to the Administration of Substances and Removal of Blood,
intravenous (IV) injection therefore these routes of drug administration are encouraged in these larger animals unless there is a good and justifiable reason to use the IP route of drug administration.
Tables 2 and 3 display the response of the different animals treated at seizure onset or 40 min. after seizure onset, respectively, with the varying doses of midazolam by the different routes of administration. As can be seen, there were increasing numbers of animals within a group displaying an anticonvulsant response as the treatment dose of midazolam was increased, regardless of route of
Many research programmes require the administration of substances to laboratory species. The effect of this on the animals concerned may be minimal or profound, depending on the substance itself, the formulation, the volume, the frequency of dosing and the skill of
Only some administration routes, techniques and guidelines for sites of administration, preparation of sites, injection techniques, and safe injection volumes will be described here.
Administration of substances to laboratory animals routes
Routes of administration EdCaN
Start studying 8- Routes of Administration of Drugs. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Tables 2 and 3 display the response of the different animals treated at seizure onset or 40 min. after seizure onset, respectively, with the varying doses of midazolam by the different routes of administration. As can be seen, there were increasing numbers of animals within a group displaying an anticonvulsant response as the treatment dose of midazolam was increased, regardless of route of
Route of drug Administration D.Raju , M.pharm , Lecturer. PHL‐358‐PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS‐I. Objectives • Describe the pharmacokinetic implications • of various Routes of Administration • • Understand the advantages and • disadvantage of various Routes of • Administration from a PK point of view • Routes
Routes of Drug Administration If you require medication, for whatever ailment, when taking a medication due to whatever aliment, the drug administration can vary depending on various circumstances, for example, the desired effect of the medication, whether the medication is intended to be local (aimed at a specific areaof the body) or systemic (aimed at the whole body), as well as the …
Other routes may require anesthesia of the animal and post-administration pain relief. Regardless of administration method used, be sure all materials are prepared before restraining animals. Aqueous materials are easier to inject than thicker materials, such as oil-based compounds.
Drugs are effective only if they reach their site of action. This is usually achieved by oral administration, but other routes are possible. Here I describe the uses and characteristic adverse
The route of administration is defined as the path by which a drug or other substance enters the body. The pharmacokinetic properties, such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, of a drug are critically influenced by the route of administration.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, 15–23 (2001) A Good Practice Guide to the Administration of Substances and Removal of Blood,
Drug Administration Routes MeSH Result
training.gov.au RTE3712A – Administer medication to animals
The Office of Animal Welfare Assurance (OAWA) is the administrative unit that helps the IACUC fulfill its institutional, regulatory, and oversight responsibilities. In addition, OAWA provides customer service to all participants of the Duke Animal Care and Use Program.
These drugs should be used very carefully in older animals or in animals with cardiac or respiratory disease. Cushing syndrome can be easily induced in small or medium-sized dogs with chronic use of potent topical steroids.
Oral solutions provide a convenient means of drug administration to neonates and young animals. A suspension is a coarse dispersion of insoluble drug particles, generally with a diameter >1 μm, in a liquid (usually aqueous) medium.
Administration of medication in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is carried out in the full cognisance of relevant regulations, and veterinary drug legislative requirements 2.3 Medication use in the treatment of infection, disease or injury is in line with the recommended dose rate/limits.
Rectal administration uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum’s blood vessels, and flow into the body’s circulatory system, which distributes the drug to the body’s organs and bodily systems.
Drug Administration Routes refers to the various ways of inserting a drug or other chemical inside a patient or animal in order for the chemical to be absorbed into the blood and delivered to the target tissue. There are several known ways to administer drug into an organism, but the easiest and the most commonly used method is through injection.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, 15–23 (2001) A Good Practice Guide to the Administration of Substances and Removal of Blood,
Remote injection is not commonly used for drug administration to fully domesticated ruminants, however this is an important method of drug administration for non-domesticated animals, both captive and free-living.
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
Discuss common adverse effects which may occur during intraventricular drug administration and strategies to prevent and manage these issues. Summarise the evidence based post procedural care of the person following intraventricular administration of an antineoplastic agent.
Routes of administration wellness.com
Veterinary Medicine Administration EPRUMA
Drugs are effective only if they reach their site of action. This is usually achieved by oral administration, but other routes are possible. Here I describe the uses and characteristic adverse
Types of treatments and treating animals Animal physiology 3 Normal physiological values 3 Reasons for abnormal physiological values 3 Other factors to observe 5 Medical treatments 6 Factors affecting treatment 6 Route of administration 6 Local and systemic effects of medication 7 Ways of giving medication 7 Forms of medications and treatments 8 Topical medication 17 Ocular …
intravenous (IV) injection therefore these routes of drug administration are encouraged in these larger animals unless there is a good and justifiable reason to use the IP route of drug administration.
Discuss common adverse effects which may occur during intraventricular drug administration and strategies to prevent and manage these issues. Summarise the evidence based post procedural care of the person following intraventricular administration of an antineoplastic agent.
Drug administration through the skin. It can achieve systemic effects but rate of absorption can vary markedly depending on the physical characteristics of the skin at application. It can achieve systemic effects but rate of absorption can vary markedly depending on …
Start studying 8- Routes of Administration of Drugs. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
To briefly review the methods, assumptions, models, accomplishments, drawbacks, and future directions of research using drug self-administration in animals and humans. Background The use of drug self-administration to study addiction is based on the assumption that drugs reinforce the behavior that results in their delivery.
Rectal administration uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum’s blood vessels, and flow into the body’s circulatory system, which distributes the drug to the body’s organs and bodily systems.

Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals : R outes of Drug A dministration to Laboratory A nimals Common routes: 1.Gastrointestinal Oral (per os) – through the mouth Gavage – into the stomach via a tube or gavage needle Rectal (per rectum) – into the rectum via the anus NPO (nil per os) – nothing by mouth.
Administration of Medication in Reptiles LafeberVet
Administration of Substances Procedures With Care
Administration of substances to laboratory animals is often necessary as part of an experimental protocol or for therapeutic reasons. The considerations and procedures that surround substance administration may affect animal welfare and the scientific validity of experimental results.
Administration of Medication in Reptiles LafeberVet
Routes of drug administration Uses and adverse effects
Tables 2 and 3 display the response of the different animals treated at seizure onset or 40 min. after seizure onset, respectively, with the varying doses of midazolam by the different routes of administration. As can be seen, there were increasing numbers of animals within a group displaying an anticonvulsant response as the treatment dose of midazolam was increased, regardless of route of
Clinical Practice Procedures Drug administration/Intranasal
Injection of Laboratory Animals Thiel College
Other routes of administration must be scientifically justified. Methylcellulose is a stable sugar with low toxicity and one of the safest and most widely used vehicles available when administered per os. Characteristics of methylcellulose affecting its viscosity include percentage and cp grade which must be considered when administered to animals.
Routes of Drug Administration to Laboratory Animals
Policy #9904 Intraperitoneal Drug Administration in
Remote injection is not commonly used for drug administration to fully domesticated ruminants, however this is an important method of drug administration for non-domesticated animals, both captive and free-living.
Routes of drug entry Processing the Environment MCAT