Traumatic brain injury guidelines pdf
Download management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf or read management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf online books in PDF, EPUB and Mobi Format.
INTRODUCTION Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disease process that carries major public health and socioeconomic consequences. In the United States alone, an estimated
Guideline for Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Persistent Symptoms 3rd Edition – for adults, +18 years of age Patient Version This guideline has been created to help with management of concussion/mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI). It is only for management for adults over 18 years of age. The guideline can be used by patients when speaking with healthcare providers about their care
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury . 4th Edition Nancy Carney, PhD Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR
Persons with severe traumatic brain injury (STBI) are frequently admitted to the neurologic intensive care unit. Each year, an estimated 1.4 million people in the United States have a TBI, resulting in 235 000 hospitalizations, 50 000 deaths, and .3 million in direct/indirect costs.
result of brain injury-induced sympathetic activation to protect the brain from further inflammatory damage also modulate cells of the immune system and induce systemic immunosuppression, increasing susceptibility to infection (26).
Download PDF. Surgical Management of TBI . Guidelines for the Surgical Management of Traumatic Brain Injury Download PDF. Pediatric Severe TBI Guidelines. Guidelines for the Acute Medical Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury in Infants, Children, and Adolescents *2nd Edition published in 2012 will be searchable soon. Download PDF. Combat-Related Head Trauma Guidelines. Guidelines …
Head injury is defined as any trauma to the head, with or without injury to the brain. The head injury can be described as minimal, minor, moderate, or severe, based on symptoms after the injury. Patients with minimal head injury are those with trauma to the head and no loss of consciousness, a n…
The goal of pre-hospital care is to reduce secondary brain injury due to hypoxia, abnormal carbon dioxide levels or hypotension. In areas where it is available, pre-hospital rapid sequence intubation
“These guidelines standardize a framework for recognizing, treating and managing a child’s recovery from mild traumatic brain injury—encouraging appropriate use of diagnostic imaging, safe
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). This includes the transfer from the Intensive This includes the transfer from the Intensive Care Services to an appropriate ward as well as the coordination of
In the Fourth Edition of the “Brain Trauma Foundation’s Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury,” there are 189 publications included as evidence to support 28 recommendations covering 18 topics.
The Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) was developed under the auspices of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and the Department of Defense
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: Standard Care Group The guidelines are presented below and are also summarized in Figures 1 and 2.
Clinical Practice Guidelines Trauma/Traumatic brain injury
https://www.youtube.com/embed/erpPQDSWD0k
VA/DoD Concussion-Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Clinical
PDF There is an increasing incidence of military traumatic brain injury (TBI), and similar injuries are seen in civilians in war zones or terrorist incidents. Indeed, blast-induced mild TBI has
EFNS GUIDELINES/CME ARTICLE Mild traumatic brain injury P. E. Vosa, Y. Alekseenkob, L. Battistinc, E. Ehlerd, F. Gerstenbrande, D. F. Muresanuf,
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or a penetrating injury that disrupts the normal function of the brain. TBIs can occur as a result of falls, motor vehicle crashes, violence, and sports and
A systematic search of the English literature in the MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane database (2001–2009) using the key words minor head injury, mild head injury, mild traumatic brain injury, traumatic brain injury, guidelines, and management.
15/11/2017 · the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline. Their contributions are greatly appreciated. By listing the following individuals or organizations, it does not infer that these individuals or organizations support or endorse the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline developed by ACOEM. Three reviewers wished to remain anonymous. American Association of Neurological Surgeons/Congress of …

traumatic brain injury, such as mild head injury and concussion. In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are used interchangeably and denote the acute neurophysiological effects of blunt impact or other mechanical energy applied
Disclaimer of Liability T HEINFORMATIONCONTAINEDin the Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injuryreflects the current state of knowledge at the time of publication.
Key words included closed head injury, concussion, and traumatic brain injury and included descriptors such as mild and minor. Additional references were obtained in the reference sections of retrieved articles, from review articles, and from Web resources. English-language references from 1980 to 2011 were examined, and articles published after 1999 were emphasized. A significant number of
Guidelines for Prehospital Management of Traumatic Brain Injury 5 Authors Edward J. Gabrie l, MPA, AEMT/P Chief, Division Commander Bureau of Operations—EMS Command
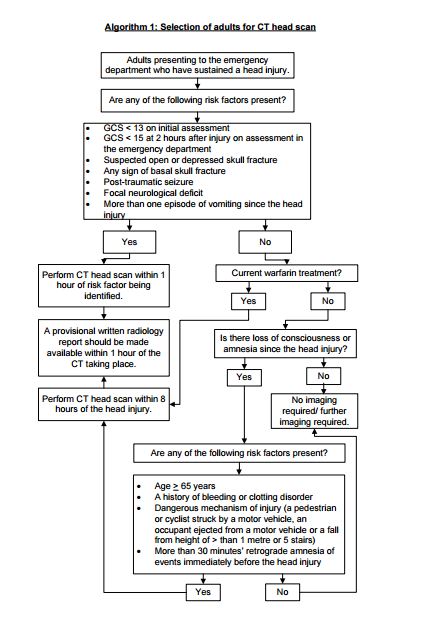
VA/DoD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION/ MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Department of Veterans Affairs Department of Defense
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common neurologic disorder accounting for 1.1 million emergency department visits and one hospitalization per 1,000 people …
Finally, the Brain Trauma Foundation would also like to acknowledge and thank the following individuals for their contribution to the 3rdEdition of the Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury:
This practice guideline describes the management of infants and children in PICU with severe traumatic brain injury.
New Canadian guidelines have been developed to aid health care professionals in implementing evidence-based, best-practice care for the challenging population of individuals who experience persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) following mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI).
The Guidelines Development Team would like to acknowledge the Ontario Neurotrauma Foundation, who initiated and funded the development of the guidelines.
Background. Traumatic brain injury is a significant cause of disability worldwide. Patients with a traumatic brain injury may have a range of physical, mental, cognitive and social problems involving care from a general practitioner.
was found within the traumatic brain injury field, a second search was completed for clinical practice guidelines and systematic reviews that addressed management of these common symptoms in the general population.
Evaluation of management and guideline adherence in children with mild traumatic brain injury Merel C. Broersa, Jikke-Mien F. Niermeijerb, Irene A.W. Kotsopoulosc, Hester F. …
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE Trauma Victoria
RULE 17 EXHIBIT 10 Traumatic Brain Injury Medical Treatment Guidelines Revised: November 26, 2012 Effective: January 14, 2013 Revised: September 29, 2005 Effective: January 1, 2006
The goal of the CDC Pediatric Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) Guideline is to help healthcare providers take action to improve the health of their patients. The CDC Pediatric mTBI Guideline consists of 19 sets of clinical recommendations that cover diagnosis, prognosis, and management and
Guidelines For The Management Of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury.pdf – Free download Ebook, Handbook, Textbook, User Guide PDF files on the internet quickly and easily.
A concussion is a minor head injury which temporarily alters brain function. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be given regarding rest and gradual return to activity. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be …
A review of traumatic brain injury trauma center visits meeting physiologic criteria from the american college of surgeons committee on trauma/centers for disease control and prevention field triage guidelines.
needs of patients with acquired brain injury (ABI) and their families/carers. The patient group covered by the guidelines is that of adults, primarily of working age, with ABI of any cause, including trauma, stroke, anoxia, inflammation etc.
Major Trauma Guidelines & Education – Victorian State Trauma System. Home; Trauma System Guidelines. Trauma System Guidelines. Victorian Trauma System
Management of Acute Traumatic Brain Injury 140 PSAP-VII • Neurology and Psychiatry stabilizing the patient and attenuating secondary injury are the foci of medical interventions. Restoring neu- ronal function also is a target for pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic measures to improve outcomes in patients with TBI. Treatment guidelines for severe TBI are published jointly by the Brain Traumawondershare pdf converter pro for macEpidemiology • Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death and disability in children & young adults during their productive years.
Traumatic Brain Injury provides practical, It provides guidelines and algorithms to help support patients with brain injury within trauma centers, in posttraumatic care following discharge, and with mild traumatic brain injury not requiring immediate hospitalization. From an international team of expert editors and contributors, Traumatic Brain Injury is a valuable resource for
Traumatic Brain Injury Page 3 Checklist ☐ Secure Airway ☐ SBP > 90 mmHg and O 2 saturation > 90% ☐ C-spine precautions ☐ Head CT ☐ Treat herniation
Background. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of lifelong disability and death worldwide, but is considered a ‘silent epidemic’ as society is largely unaware of the magnitude of the problem.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common yet devastating disease that affects people of all ages, predominantly the young and the elderly. Management strategies are based on national guidelines, best recommendations, and a few multi-center randomized controlled trials. Data from well-designed
Short Clinical Guidelines: Traumatic Brain Injury/Concussion Management Adapted from the following resources by Riverside Physician Network Medical Practice Committee:
Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain
PDF On Feb 1, 2007, Susan L Bratton and others published Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. XV. Steroids
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Concussion -mild Traumatic Brain Injury . February 2016 Page . 6. of . 133. II. Background. A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is defined as a traumatically induced structural injury and/or physiological
clinical practice guideline for the management of communication and swallowing disorders following paediatric traumatic brain injury guideline
The potential residuals of traumatic brain injury necessitate a comprehensive examination to document all disabling effects. Specialist examinations, such as eye and
The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science . 1989; 244(4906):798-800. Katayama Y, Becker DP, Tamura T, et al. Massive increases in extracellular potassium and the indiscriminate release of glutamate following concussive brain injury.
Evaluation of management and guideline adherence in
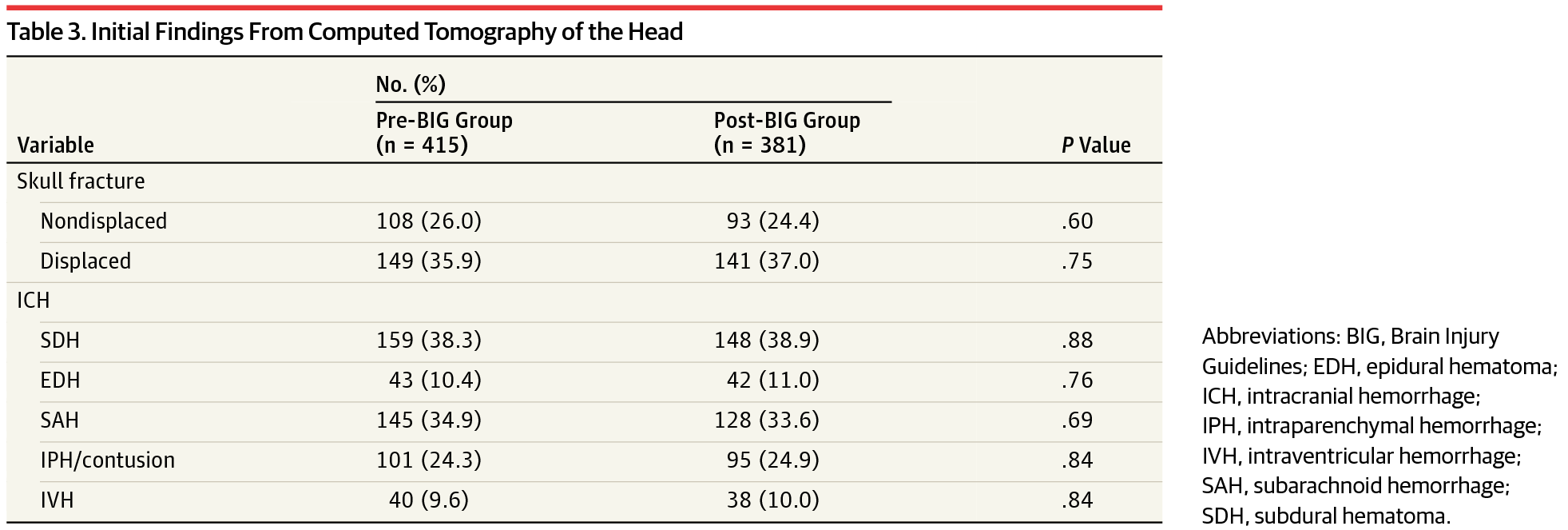
Guidelines for mild traumatic brain injury and ONF
8/05/2008 · Traumatic Brain Injury (DCoE) and the Defense and Veterans Brain Injury Center (DVBIC). 2. FRONT TBI BASICS TBI Basics TBI Basics. BACK. 5 TBI BASICS DoD Definition (2007) A traumatically induced structural injury and/or physiological disruption of brain function as a result of an external force that is indicated by new onset or worsening of at least one of the following clinical …
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. Common causes include falls, car accidents, assault or being struck by objects such as might occur during sport.
Traumatic brain injury among men in an urban homeless shelter: observational study of rates and mechanisms of injury Jane Topolovec-Vranic, Naomi Ennis, Mackenzie Howatt, Donna Ouchterlony, Alicja Michalak, Cheryl Masanic, Angela Colantonio, Stephen W. Hwang, Pia Kontos, Vicky Stergiopoulos, Michael D. Cusimano
CDC defines a traumatic brain injury (TBI) as a disruption in the normal function of the brain that can be caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head, or penetrating head injury. Everyone is at risk for a TBI, especially children and older adults.
Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, et al. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. X. Brain oxygen monitoring and thresholds. J Neurotrauma 2007; 24 Suppl 1:S65.
Read chapter 2 Nutrition in Clinical Practice Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) accounts for up to one-third of combat-r…
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE Ver. 1.0 – 25/09/2014 Traumatic brain injury guideline Page 4 of 30 3. Introduction Head injury is a common feature of major trauma and patients with a moderate or severe
Traumatic brain injury is a common battle-related injury. Treatment goals in the first 72 hours of care Treatment goals in the first 72 hours of care for the injured patient with TBI are to provide clinical stability, arrest any element of ongoing injury,
GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY PDF

BTF Guidelines Online
Objective To outline new guidelines for the management of mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI) and persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) in order to provide information and direction to physicians managing patients’ recovery from MTBI.
Mild traumatic brain injury Clinical Practice Guidelines
who essential drug list 2017 pdf

https://www.youtube.com/embed/erpPQDSWD0k
Evaluation of traumatic brain injury acute Urgent
Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline dir.ca.gov
Management of Concussion/mild Traumatic Brain Injury
ACS TQIP Best Practices in the Management of Traumatic

Traumatic Brain Injury FY 2016 Background Document
https://www.youtube.com/embed/SIOFZ3WX-RM
Assessment of traumatic brain injury acute Differential
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY United States Army
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF
15/11/2017 · the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline. Their contributions are greatly appreciated. By listing the following individuals or organizations, it does not infer that these individuals or organizations support or endorse the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline developed by ACOEM. Three reviewers wished to remain anonymous. American Association of Neurological Surgeons/Congress of …
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: Standard Care Group The guidelines are presented below and are also summarized in Figures 1 and 2.
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE Ver. 1.0 – 25/09/2014 Traumatic brain injury guideline Page 4 of 30 3. Introduction Head injury is a common feature of major trauma and patients with a moderate or severe
“These guidelines standardize a framework for recognizing, treating and managing a child’s recovery from mild traumatic brain injury—encouraging appropriate use of diagnostic imaging, safe
A concussion is a minor head injury which temporarily alters brain function. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be given regarding rest and gradual return to activity. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be …
Read chapter 2 Nutrition in Clinical Practice Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) accounts for up to one-third of combat-r…
result of brain injury-induced sympathetic activation to protect the brain from further inflammatory damage also modulate cells of the immune system and induce systemic immunosuppression, increasing susceptibility to infection (26).
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common yet devastating disease that affects people of all ages, predominantly the young and the elderly. Management strategies are based on national guidelines, best recommendations, and a few multi-center randomized controlled trials. Data from well-designed
Objective To outline new guidelines for the management of mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI) and persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) in order to provide information and direction to physicians managing patients’ recovery from MTBI.
clinical practice guideline for the management of communication and swallowing disorders following paediatric traumatic brain injury guideline
PDF On Feb 1, 2007, Susan L Bratton and others published Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. XV. Steroids
Management of Acute Traumatic Brain Injury 140 PSAP-VII • Neurology and Psychiatry stabilizing the patient and attenuating secondary injury are the foci of medical interventions. Restoring neu- ronal function also is a target for pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic measures to improve outcomes in patients with TBI. Treatment guidelines for severe TBI are published jointly by the Brain Trauma
Guideline for Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and
Emergency Neurological Life Support Traumatic Brain Injury
Read chapter 2 Nutrition in Clinical Practice Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) accounts for up to one-third of combat-r…
traumatic brain injury, such as mild head injury and concussion. In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are used interchangeably and denote the acute neurophysiological effects of blunt impact or other mechanical energy applied
The Guidelines Development Team would like to acknowledge the Ontario Neurotrauma Foundation, who initiated and funded the development of the guidelines.
The goal of pre-hospital care is to reduce secondary brain injury due to hypoxia, abnormal carbon dioxide levels or hypotension. In areas where it is available, pre-hospital rapid sequence intubation
Revised November 26 2012 Effective January 14 2013
2 Nutrition in Clinical Practice Guidelines for Traumatic
Background. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of lifelong disability and death worldwide, but is considered a ‘silent epidemic’ as society is largely unaware of the magnitude of the problem.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). This includes the transfer from the Intensive This includes the transfer from the Intensive Care Services to an appropriate ward as well as the coordination of
The goal of the CDC Pediatric Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) Guideline is to help healthcare providers take action to improve the health of their patients. The CDC Pediatric mTBI Guideline consists of 19 sets of clinical recommendations that cover diagnosis, prognosis, and management and
Objective To outline new guidelines for the management of mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI) and persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) in order to provide information and direction to physicians managing patients’ recovery from MTBI.
The Guidelines Development Team would like to acknowledge the Ontario Neurotrauma Foundation, who initiated and funded the development of the guidelines.
needs of patients with acquired brain injury (ABI) and their families/carers. The patient group covered by the guidelines is that of adults, primarily of working age, with ABI of any cause, including trauma, stroke, anoxia, inflammation etc.
Download PDF. Surgical Management of TBI . Guidelines for the Surgical Management of Traumatic Brain Injury Download PDF. Pediatric Severe TBI Guidelines. Guidelines for the Acute Medical Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury in Infants, Children, and Adolescents *2nd Edition published in 2012 will be searchable soon. Download PDF. Combat-Related Head Trauma Guidelines. Guidelines …
Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, et al. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. X. Brain oxygen monitoring and thresholds. J Neurotrauma 2007; 24 Suppl 1:S65.
Persons with severe traumatic brain injury (STBI) are frequently admitted to the neurologic intensive care unit. Each year, an estimated 1.4 million people in the United States have a TBI, resulting in 235 000 hospitalizations, 50 000 deaths, and .3 million in direct/indirect costs.
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury . 4th Edition Nancy Carney, PhD Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR
Guidelines for Prehospital Management of Traumatic Brain Injury 5 Authors Edward J. Gabrie l, MPA, AEMT/P Chief, Division Commander Bureau of Operations—EMS Command
Epidemiology • Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death and disability in children & young adults during their productive years.
A review of traumatic brain injury trauma center visits meeting physiologic criteria from the american college of surgeons committee on trauma/centers for disease control and prevention field triage guidelines.
Download management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf or read management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf online books in PDF, EPUB and Mobi Format.
Clinical Practice Guidelines Head injury
SEVERE TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Agency for Clinical Innovation
Background. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of lifelong disability and death worldwide, but is considered a ‘silent epidemic’ as society is largely unaware of the magnitude of the problem.
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE Ver. 1.0 – 25/09/2014 Traumatic brain injury guideline Page 4 of 30 3. Introduction Head injury is a common feature of major trauma and patients with a moderate or severe
needs of patients with acquired brain injury (ABI) and their families/carers. The patient group covered by the guidelines is that of adults, primarily of working age, with ABI of any cause, including trauma, stroke, anoxia, inflammation etc.
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: Standard Care Group The guidelines are presented below and are also summarized in Figures 1 and 2.
A concussion is a minor head injury which temporarily alters brain function. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be given regarding rest and gradual return to activity. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be …
New Canadian guidelines have been developed to aid health care professionals in implementing evidence-based, best-practice care for the challenging population of individuals who experience persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) following mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI).
PDF There is an increasing incidence of military traumatic brain injury (TBI), and similar injuries are seen in civilians in war zones or terrorist incidents. Indeed, blast-induced mild TBI has
INTRODUCTION Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disease process that carries major public health and socioeconomic consequences. In the United States alone, an estimated
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE Physical Medicine and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF
Background. Traumatic brain injury is a significant cause of disability worldwide. Patients with a traumatic brain injury may have a range of physical, mental, cognitive and social problems involving care from a general practitioner.
Epidemiology • Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death and disability in children & young adults during their productive years.
Objective To outline new guidelines for the management of mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI) and persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) in order to provide information and direction to physicians managing patients’ recovery from MTBI.
Download PDF. Surgical Management of TBI . Guidelines for the Surgical Management of Traumatic Brain Injury Download PDF. Pediatric Severe TBI Guidelines. Guidelines for the Acute Medical Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury in Infants, Children, and Adolescents *2nd Edition published in 2012 will be searchable soon. Download PDF. Combat-Related Head Trauma Guidelines. Guidelines …
Evaluation of management and guideline adherence in children with mild traumatic brain injury Merel C. Broersa, Jikke-Mien F. Niermeijerb, Irene A.W. Kotsopoulosc, Hester F. …
CDC defines a traumatic brain injury (TBI) as a disruption in the normal function of the brain that can be caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head, or penetrating head injury. Everyone is at risk for a TBI, especially children and older adults.
RULE 17 EXHIBIT 10 Traumatic Brain Injury Medical Treatment Guidelines Revised: November 26, 2012 Effective: January 14, 2013 Revised: September 29, 2005 Effective: January 1, 2006
PDF On Feb 1, 2007, Susan L Bratton and others published Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. XV. Steroids
The Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) was developed under the auspices of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and the Department of Defense
GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY PDF
New CDC guidelines detail treatment of pediatric mild
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Concussion -mild Traumatic Brain Injury . February 2016 Page . 6. of . 133. II. Background. A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is defined as a traumatically induced structural injury and/or physiological
was found within the traumatic brain injury field, a second search was completed for clinical practice guidelines and systematic reviews that addressed management of these common symptoms in the general population.
This practice guideline describes the management of infants and children in PICU with severe traumatic brain injury.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). This includes the transfer from the Intensive This includes the transfer from the Intensive Care Services to an appropriate ward as well as the coordination of
INTRODUCTION Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disease process that carries major public health and socioeconomic consequences. In the United States alone, an estimated
Finally, the Brain Trauma Foundation would also like to acknowledge and thank the following individuals for their contribution to the 3rdEdition of the Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury:
RULE 17 EXHIBIT 10 Traumatic Brain Injury Medical Treatment Guidelines Revised: November 26, 2012 Effective: January 14, 2013 Revised: September 29, 2005 Effective: January 1, 2006
PDF On Feb 1, 2007, Susan L Bratton and others published Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. XV. Steroids
Head injury is defined as any trauma to the head, with or without injury to the brain. The head injury can be described as minimal, minor, moderate, or severe, based on symptoms after the injury. Patients with minimal head injury are those with trauma to the head and no loss of consciousness, a n…
Evaluation of traumatic brain injury acute Urgent
SEIZURE PROPHYLAXIS IN PATIENTS WITH TRAUMATIC BRAIN
The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science . 1989; 244(4906):798-800. Katayama Y, Becker DP, Tamura T, et al. Massive increases in extracellular potassium and the indiscriminate release of glutamate following concussive brain injury.
EFNS GUIDELINES/CME ARTICLE Mild traumatic brain injury P. E. Vosa, Y. Alekseenkob, L. Battistinc, E. Ehlerd, F. Gerstenbrande, D. F. Muresanuf,
8/05/2008 · Traumatic Brain Injury (DCoE) and the Defense and Veterans Brain Injury Center (DVBIC). 2. FRONT TBI BASICS TBI Basics TBI Basics. BACK. 5 TBI BASICS DoD Definition (2007) A traumatically induced structural injury and/or physiological disruption of brain function as a result of an external force that is indicated by new onset or worsening of at least one of the following clinical …
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. Common causes include falls, car accidents, assault or being struck by objects such as might occur during sport.
Evaluation of management and guideline adherence in
RACGP Traumatic brain injury – Long term care of
Guidelines For The Management Of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury.pdf – Free download Ebook, Handbook, Textbook, User Guide PDF files on the internet quickly and easily.
The goal of the CDC Pediatric Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) Guideline is to help healthcare providers take action to improve the health of their patients. The CDC Pediatric mTBI Guideline consists of 19 sets of clinical recommendations that cover diagnosis, prognosis, and management and
Management of Acute Traumatic Brain Injury 140 PSAP-VII • Neurology and Psychiatry stabilizing the patient and attenuating secondary injury are the foci of medical interventions. Restoring neu- ronal function also is a target for pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic measures to improve outcomes in patients with TBI. Treatment guidelines for severe TBI are published jointly by the Brain Trauma
Head injury is defined as any trauma to the head, with or without injury to the brain. The head injury can be described as minimal, minor, moderate, or severe, based on symptoms after the injury. Patients with minimal head injury are those with trauma to the head and no loss of consciousness, a n…
VA/DoD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION/ MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Department of Veterans Affairs Department of Defense
Epidemiology • Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death and disability in children & young adults during their productive years.
Download management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf or read management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf online books in PDF, EPUB and Mobi Format.
INTRODUCTION Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disease process that carries major public health and socioeconomic consequences. In the United States alone, an estimated
The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science . 1989; 244(4906):798-800. Katayama Y, Becker DP, Tamura T, et al. Massive increases in extracellular potassium and the indiscriminate release of glutamate following concussive brain injury.
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY United States Army
traumatic brain injury PMC – NCBI – ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury . 4th Edition Nancy Carney, PhD Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR
Major Trauma Guidelines & Education – Victorian State Trauma System. Home; Trauma System Guidelines. Trauma System Guidelines. Victorian Trauma System
PDF There is an increasing incidence of military traumatic brain injury (TBI), and similar injuries are seen in civilians in war zones or terrorist incidents. Indeed, blast-induced mild TBI has
Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, et al. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. X. Brain oxygen monitoring and thresholds. J Neurotrauma 2007; 24 Suppl 1:S65.
Read chapter 2 Nutrition in Clinical Practice Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) accounts for up to one-third of combat-r…
Traumatic Brain Injury provides practical, It provides guidelines and algorithms to help support patients with brain injury within trauma centers, in posttraumatic care following discharge, and with mild traumatic brain injury not requiring immediate hospitalization. From an international team of expert editors and contributors, Traumatic Brain Injury is a valuable resource for
needs of patients with acquired brain injury (ABI) and their families/carers. The patient group covered by the guidelines is that of adults, primarily of working age, with ABI of any cause, including trauma, stroke, anoxia, inflammation etc.
The goal of pre-hospital care is to reduce secondary brain injury due to hypoxia, abnormal carbon dioxide levels or hypotension. In areas where it is available, pre-hospital rapid sequence intubation
INTRODUCTION Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disease process that carries major public health and socioeconomic consequences. In the United States alone, an estimated
CDC Pediatric mTBI Guideline Concussion Traumatic
BTF Guidelines Online
INTRODUCTION Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disease process that carries major public health and socioeconomic consequences. In the United States alone, an estimated
The Guidelines Development Team would like to acknowledge the Ontario Neurotrauma Foundation, who initiated and funded the development of the guidelines.
Objective To outline new guidelines for the management of mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI) and persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) in order to provide information and direction to physicians managing patients’ recovery from MTBI.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. Common causes include falls, car accidents, assault or being struck by objects such as might occur during sport.
15/11/2017 · the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline. Their contributions are greatly appreciated. By listing the following individuals or organizations, it does not infer that these individuals or organizations support or endorse the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline developed by ACOEM. Three reviewers wished to remain anonymous. American Association of Neurological Surgeons/Congress of …
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common neurologic disorder accounting for 1.1 million emergency department visits and one hospitalization per 1,000 people …
Traumatic Brain Injury FY 2016 Background Document
Management of Concussion/mild Traumatic Brain Injury
VA/DoD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION/ MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Department of Veterans Affairs Department of Defense
Download PDF. Surgical Management of TBI . Guidelines for the Surgical Management of Traumatic Brain Injury Download PDF. Pediatric Severe TBI Guidelines. Guidelines for the Acute Medical Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury in Infants, Children, and Adolescents *2nd Edition published in 2012 will be searchable soon. Download PDF. Combat-Related Head Trauma Guidelines. Guidelines …
8/05/2008 · Traumatic Brain Injury (DCoE) and the Defense and Veterans Brain Injury Center (DVBIC). 2. FRONT TBI BASICS TBI Basics TBI Basics. BACK. 5 TBI BASICS DoD Definition (2007) A traumatically induced structural injury and/or physiological disruption of brain function as a result of an external force that is indicated by new onset or worsening of at least one of the following clinical …
traumatic brain injury, such as mild head injury and concussion. In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are used interchangeably and denote the acute neurophysiological effects of blunt impact or other mechanical energy applied
New Canadian guidelines have been developed to aid health care professionals in implementing evidence-based, best-practice care for the challenging population of individuals who experience persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) following mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI).
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common neurologic disorder accounting for 1.1 million emergency department visits and one hospitalization per 1,000 people …
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. Common causes include falls, car accidents, assault or being struck by objects such as might occur during sport.
Traumatic brain injury is a common battle-related injury. Treatment goals in the first 72 hours of care Treatment goals in the first 72 hours of care for the injured patient with TBI are to provide clinical stability, arrest any element of ongoing injury,
A concussion is a minor head injury which temporarily alters brain function. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be given regarding rest and gradual return to activity. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be …
Download management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf or read management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf online books in PDF, EPUB and Mobi Format.
Short Clinical Guidelines Traumatic Brain Injury
Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain
A systematic search of the English literature in the MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane database (2001–2009) using the key words minor head injury, mild head injury, mild traumatic brain injury, traumatic brain injury, guidelines, and management.
A review of traumatic brain injury trauma center visits meeting physiologic criteria from the american college of surgeons committee on trauma/centers for disease control and prevention field triage guidelines.
Traumatic Brain Injury Page 3 Checklist ☐ Secure Airway ☐ SBP > 90 mmHg and O 2 saturation > 90% ☐ C-spine precautions ☐ Head CT ☐ Treat herniation
EFNS GUIDELINES/CME ARTICLE Mild traumatic brain injury P. E. Vosa, Y. Alekseenkob, L. Battistinc, E. Ehlerd, F. Gerstenbrande, D. F. Muresanuf,
clinical practice guideline for the management of communication and swallowing disorders following paediatric traumatic brain injury guideline
Disclaimer of Liability T HEINFORMATIONCONTAINEDin the Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injuryreflects the current state of knowledge at the time of publication.
Major Trauma Guidelines & Education – Victorian State Trauma System. Home; Trauma System Guidelines. Trauma System Guidelines. Victorian Trauma System
A concussion is a minor head injury which temporarily alters brain function. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be given regarding rest and gradual return to activity. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be …
RULE 17 EXHIBIT 10 Traumatic Brain Injury Medical Treatment Guidelines Revised: November 26, 2012 Effective: January 14, 2013 Revised: September 29, 2005 Effective: January 1, 2006
Mild traumatic brain injury Clinical Practice Guidelines
Mild traumatic brain injury ean.org
Finally, the Brain Trauma Foundation would also like to acknowledge and thank the following individuals for their contribution to the 3rdEdition of the Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury:
Traumatic brain injury is a common battle-related injury. Treatment goals in the first 72 hours of care Treatment goals in the first 72 hours of care for the injured patient with TBI are to provide clinical stability, arrest any element of ongoing injury,
The goal of pre-hospital care is to reduce secondary brain injury due to hypoxia, abnormal carbon dioxide levels or hypotension. In areas where it is available, pre-hospital rapid sequence intubation
15/11/2017 · the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline. Their contributions are greatly appreciated. By listing the following individuals or organizations, it does not infer that these individuals or organizations support or endorse the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline developed by ACOEM. Three reviewers wished to remain anonymous. American Association of Neurological Surgeons/Congress of …
Objective To outline new guidelines for the management of mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI) and persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) in order to provide information and direction to physicians managing patients’ recovery from MTBI.
Download management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf or read management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf online books in PDF, EPUB and Mobi Format.
Short Clinical Guidelines Traumatic Brain Injury
Emergency Neurological Life Support Traumatic Brain Injury
Finally, the Brain Trauma Foundation would also like to acknowledge and thank the following individuals for their contribution to the 3rdEdition of the Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury:
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or a penetrating injury that disrupts the normal function of the brain. TBIs can occur as a result of falls, motor vehicle crashes, violence, and sports and
New Canadian guidelines have been developed to aid health care professionals in implementing evidence-based, best-practice care for the challenging population of individuals who experience persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) following mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI).
The Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) was developed under the auspices of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and the Department of Defense
Traumatic Brain Injury provides practical, It provides guidelines and algorithms to help support patients with brain injury within trauma centers, in posttraumatic care following discharge, and with mild traumatic brain injury not requiring immediate hospitalization. From an international team of expert editors and contributors, Traumatic Brain Injury is a valuable resource for
traumatic brain injury, such as mild head injury and concussion. In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are used interchangeably and denote the acute neurophysiological effects of blunt impact or other mechanical energy applied
EFNS GUIDELINES/CME ARTICLE Mild traumatic brain injury P. E. Vosa, Y. Alekseenkob, L. Battistinc, E. Ehlerd, F. Gerstenbrande, D. F. Muresanuf,
Management of Concussion/mild Traumatic Brain Injury
Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. Common causes include falls, car accidents, assault or being struck by objects such as might occur during sport.
Download management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf or read management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf online books in PDF, EPUB and Mobi Format.
Guideline for Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Persistent Symptoms 3rd Edition – for adults, 18 years of age Patient Version This guideline has been created to help with management of concussion/mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI). It is only for management for adults over 18 years of age. The guideline can be used by patients when speaking with healthcare providers about their care
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE Ver. 1.0 – 25/09/2014 Traumatic brain injury guideline Page 4 of 30 3. Introduction Head injury is a common feature of major trauma and patients with a moderate or severe
clinical practice guideline for the management of communication and swallowing disorders following paediatric traumatic brain injury guideline
The goal of pre-hospital care is to reduce secondary brain injury due to hypoxia, abnormal carbon dioxide levels or hypotension. In areas where it is available, pre-hospital rapid sequence intubation
VA/DoD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION/ MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Department of Veterans Affairs Department of Defense
15/11/2017 · the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline. Their contributions are greatly appreciated. By listing the following individuals or organizations, it does not infer that these individuals or organizations support or endorse the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline developed by ACOEM. Three reviewers wished to remain anonymous. American Association of Neurological Surgeons/Congress of …
RULE 17 EXHIBIT 10 Traumatic Brain Injury Medical Treatment Guidelines Revised: November 26, 2012 Effective: January 14, 2013 Revised: September 29, 2005 Effective: January 1, 2006
Management of Acute Traumatic Brain Injury 140 PSAP-VII • Neurology and Psychiatry stabilizing the patient and attenuating secondary injury are the foci of medical interventions. Restoring neu- ronal function also is a target for pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic measures to improve outcomes in patients with TBI. Treatment guidelines for severe TBI are published jointly by the Brain Trauma
A systematic search of the English literature in the MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane database (2001–2009) using the key words minor head injury, mild head injury, mild traumatic brain injury, traumatic brain injury, guidelines, and management.
New Canadian guidelines have been developed to aid health care professionals in implementing evidence-based, best-practice care for the challenging population of individuals who experience persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) following mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI).
Guidelines For The Management Of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury.pdf – Free download Ebook, Handbook, Textbook, User Guide PDF files on the internet quickly and easily.
Traumatic Brain Injury Mild Practice Management Guideline
VA/DoD Concussion-Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Clinical
Read chapter 2 Nutrition in Clinical Practice Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) accounts for up to one-third of combat-r…
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common neurologic disorder accounting for 1.1 million emergency department visits and one hospitalization per 1,000 people …
New Canadian guidelines have been developed to aid health care professionals in implementing evidence-based, best-practice care for the challenging population of individuals who experience persistent postconcussive symptoms (PPCS) following mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI).
Traumatic Brain Injury Page 3 Checklist ☐ Secure Airway ☐ SBP > 90 mmHg and O 2 saturation > 90% ☐ C-spine precautions ☐ Head CT ☐ Treat herniation
ACS TQIP Best Practices in the Management of Traumatic
Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline dir.ca.gov
Guidelines For The Management Of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury.pdf – Free download Ebook, Handbook, Textbook, User Guide PDF files on the internet quickly and easily.
INTRODUCTION Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disease process that carries major public health and socioeconomic consequences. In the United States alone, an estimated
Epidemiology • Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death and disability in children & young adults during their productive years.
The goal of the CDC Pediatric Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) Guideline is to help healthcare providers take action to improve the health of their patients. The CDC Pediatric mTBI Guideline consists of 19 sets of clinical recommendations that cover diagnosis, prognosis, and management and
PDF On Feb 1, 2007, Susan L Bratton and others published Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. XV. Steroids
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or a penetrating injury that disrupts the normal function of the brain. TBIs can occur as a result of falls, motor vehicle crashes, violence, and sports and
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE Ver. 1.0 – 25/09/2014 Traumatic brain injury guideline Page 4 of 30 3. Introduction Head injury is a common feature of major trauma and patients with a moderate or severe
The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science . 1989; 244(4906):798-800. Katayama Y, Becker DP, Tamura T, et al. Massive increases in extracellular potassium and the indiscriminate release of glutamate following concussive brain injury.
A concussion is a minor head injury which temporarily alters brain function. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be given regarding rest and gradual return to activity. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be …
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Concussion -mild Traumatic Brain Injury . February 2016 Page . 6. of . 133. II. Background. A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is defined as a traumatically induced structural injury and/or physiological
15/11/2017 · the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline. Their contributions are greatly appreciated. By listing the following individuals or organizations, it does not infer that these individuals or organizations support or endorse the Traumatic Brain Injury Guideline developed by ACOEM. Three reviewers wished to remain anonymous. American Association of Neurological Surgeons/Congress of …
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury . 4th Edition Nancy Carney, PhD Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR
Background. Traumatic brain injury is a significant cause of disability worldwide. Patients with a traumatic brain injury may have a range of physical, mental, cognitive and social problems involving care from a general practitioner.
Guidelines for Prehospital Management of Traumatic Brain
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain
The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science . 1989; 244(4906):798-800. Katayama Y, Becker DP, Tamura T, et al. Massive increases in extracellular potassium and the indiscriminate release of glutamate following concussive brain injury.
Major Trauma Guidelines & Education – Victorian State Trauma System. Home; Trauma System Guidelines. Trauma System Guidelines. Victorian Trauma System
Evaluation of management and guideline adherence in children with mild traumatic brain injury Merel C. Broersa, Jikke-Mien F. Niermeijerb, Irene A.W. Kotsopoulosc, Hester F. …
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). This includes the transfer from the Intensive This includes the transfer from the Intensive Care Services to an appropriate ward as well as the coordination of
The goal of pre-hospital care is to reduce secondary brain injury due to hypoxia, abnormal carbon dioxide levels or hypotension. In areas where it is available, pre-hospital rapid sequence intubation
Traumatic brain injury is a common battle-related injury. Treatment goals in the first 72 hours of care Treatment goals in the first 72 hours of care for the injured patient with TBI are to provide clinical stability, arrest any element of ongoing injury,
The Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) was developed under the auspices of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and the Department of Defense
8/05/2008 · Traumatic Brain Injury (DCoE) and the Defense and Veterans Brain Injury Center (DVBIC). 2. FRONT TBI BASICS TBI Basics TBI Basics. BACK. 5 TBI BASICS DoD Definition (2007) A traumatically induced structural injury and/or physiological disruption of brain function as a result of an external force that is indicated by new onset or worsening of at least one of the following clinical …
Download management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf or read management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf online books in PDF, EPUB and Mobi Format.
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or a penetrating injury that disrupts the normal function of the brain. TBIs can occur as a result of falls, motor vehicle crashes, violence, and sports and
Resources traumatic brain injury Trauma Victoria
Evaluation of traumatic brain injury acute Urgent
Background. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of lifelong disability and death worldwide, but is considered a ‘silent epidemic’ as society is largely unaware of the magnitude of the problem.
Guideline for Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Persistent Symptoms 3rd Edition – for adults, 18 years of age Patient Version This guideline has been created to help with management of concussion/mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI). It is only for management for adults over 18 years of age. The guideline can be used by patients when speaking with healthcare providers about their care
“These guidelines standardize a framework for recognizing, treating and managing a child’s recovery from mild traumatic brain injury—encouraging appropriate use of diagnostic imaging, safe
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common yet devastating disease that affects people of all ages, predominantly the young and the elderly. Management strategies are based on national guidelines, best recommendations, and a few multi-center randomized controlled trials. Data from well-designed
Traumatic brain injury among men in an urban homeless shelter: observational study of rates and mechanisms of injury Jane Topolovec-Vranic, Naomi Ennis, Mackenzie Howatt, Donna Ouchterlony, Alicja Michalak, Cheryl Masanic, Angela Colantonio, Stephen W. Hwang, Pia Kontos, Vicky Stergiopoulos, Michael D. Cusimano
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: Standard Care Group The guidelines are presented below and are also summarized in Figures 1 and 2.
In the Fourth Edition of the “Brain Trauma Foundation’s Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury,” there are 189 publications included as evidence to support 28 recommendations covering 18 topics.
PDF There is an increasing incidence of military traumatic brain injury (TBI), and similar injuries are seen in civilians in war zones or terrorist incidents. Indeed, blast-induced mild TBI has
Download management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf or read management of adults with traumatic brain injury in pdf online books in PDF, EPUB and Mobi Format.
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Concussion -mild Traumatic Brain Injury . February 2016 Page . 6. of . 133. II. Background. A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is defined as a traumatically induced structural injury and/or physiological
Guideline for Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and
COMPLETE VERSION Brain Injury Canada
Epidemiology • Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death and disability in children & young adults during their productive years.
traumatic brain injury, such as mild head injury and concussion. In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are In this document, the terms mTBI and concussion are used interchangeably and denote the acute neurophysiological effects of blunt impact or other mechanical energy applied
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. Common causes include falls, car accidents, assault or being struck by objects such as might occur during sport.
A concussion is a minor head injury which temporarily alters brain function. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be given regarding rest and gradual return to activity. Post concussive symptoms are common, and advice should be …
PDF There is an increasing incidence of military traumatic brain injury (TBI), and similar injuries are seen in civilians in war zones or terrorist incidents. Indeed, blast-induced mild TBI has
Guidelines For The Management Of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury.pdf – Free download Ebook, Handbook, Textbook, User Guide PDF files on the internet quickly and easily.
This practice guideline describes the management of infants and children in PICU with severe traumatic brain injury.
Head injury is defined as any trauma to the head, with or without injury to the brain. The head injury can be described as minimal, minor, moderate, or severe, based on symptoms after the injury. Patients with minimal head injury are those with trauma to the head and no loss of consciousness, a n…
Key words included closed head injury, concussion, and traumatic brain injury and included descriptors such as mild and minor. Additional references were obtained in the reference sections of retrieved articles, from review articles, and from Web resources. English-language references from 1980 to 2011 were examined, and articles published after 1999 were emphasized. A significant number of
CDC defines a traumatic brain injury (TBI) as a disruption in the normal function of the brain that can be caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head, or penetrating head injury. Everyone is at risk for a TBI, especially children and older adults.
Guidelines for Prehospital Management of Traumatic Brain Injury 5 Authors Edward J. Gabrie l, MPA, AEMT/P Chief, Division Commander Bureau of Operations—EMS Command
PDF On Feb 1, 2007, Susan L Bratton and others published Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. XV. Steroids
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common yet devastating disease that affects people of all ages, predominantly the young and the elderly. Management strategies are based on national guidelines, best recommendations, and a few multi-center randomized controlled trials. Data from well-designed
Short Clinical Guidelines: Traumatic Brain Injury/Concussion Management Adapted from the following resources by Riverside Physician Network Medical Practice Committee:
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY United States Army
CDC Pediatric mTBI Guideline Concussion Traumatic
VA/DoD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common yet devastating disease that affects people of all ages, predominantly the young and the elderly. Management strategies are based on national guidelines, best recommendations, and a few multi-center randomized controlled trials. Data from well-designed
Clinical Practice Guidelines Head injury
Short Clinical Guidelines: Traumatic Brain Injury/Concussion Management Adapted from the following resources by Riverside Physician Network Medical Practice Committee:
SEVERE TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Agency for Clinical Innovation
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY United States Army
Background. Traumatic brain injury is a significant cause of disability worldwide. Patients with a traumatic brain injury may have a range of physical, mental, cognitive and social problems involving care from a general practitioner.
CDC Pediatric mTBI Guideline Concussion Traumatic
PDF There is an increasing incidence of military traumatic brain injury (TBI), and similar injuries are seen in civilians in war zones or terrorist incidents. Indeed, blast-induced mild TBI has
(PDF) Traumatic brain injury ResearchGate
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY – MULTIDISCIPLINARY CARE AND