Cannabis effects on the brain pdf
How Marijuana Affects the Body and Brain Natasha Tracy Marijuana is a psychoactive drug, a preparation of the leaves and flowers of the cannabis (cannabis sativa) plant.Marijuana affects the brain and the body.
The main psychoactive ingredient of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which acts on specific receptors in the brain known as cannabinoid or CB1 receptors. 3 Research has found that the cannabis plant produces between 80 and 100 cannabinoids and about 300 non-cannabinoid chemicals.
An appreciable proportion of cannabis users report short-lived adverse effects, including psychotic states following heavy consumption, and regular users are at risk of dependence. People with major mental illnesses such as schizophrenia are especially vulnerable in that cannabis generally provokes relapse and aggravates existing symptoms. Health workers need to recognise, and respond to, the
As with studies on the acute effects of cannabis on brain functioning, most studies to date examining brain functioning among abstinent cannabis users have employed PET to examine rCBF at rest or during performance of a task. In contrast to increased brain metabolism usually observed during acute intoxication, the most consistent finding is lower brain metabolism among abstinent cannabis users
examining the potential long-term residual effects of cannabis on cognition in monozygotic male twins reported “an absence of marked long-term residual effects of marijuana use on cognitive abilities.” A …
Marijuana is known to affect functional parts of the brain when you are high. But marijuana does not only affect the brain for a shorter period of time. While some effects are completely reversible, it can also change the way our brain works. Marijuana can also impair the brain’s development in teenagers. And what most stoners don’t want to hear is:
Abstract. The active compound in herbal cannabis, Δ 9 ‐tetrahydrocannabinol, exerts all of its known central effects through the CB 1 cannabinoid receptor.
Marijuana: Cannabis’ effects on the human brain . Because cannabis is psychoactive in nature, questions naturally arise as to its possible negative effects on the human brain or brain chemistryl.
Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research University of California, San Diego Cannabis and Neuropsychiatry: Overview ! Purpose: to review the effects of cannabis on the brain and behavior
The psychoactive effects of cannabis, known as a “high”, are subjective and can vary based on the person and the method of use. When THC enters the blood stream and reaches the brain, it binds to cannabinoid receptors.
Of particular interest to many who study the effects of marijuana are its impact on the brain. Many who oppose legalization focus on the effects of the treatments, and often the focus is misguided.
The typical acute effects of cannabis resemble some of the features of schizophrenia, in particular the sensory distortions, inexplicable mirth, feelings of depersonalisation and loss of motivation.
Cannabis in the Brain and Body The active ingredient in cannabis, delta‐9‐tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), is only found in small portions of the cannabis plant, in the flowering tops and in some of the leaves.THC stimulates cannabinoid receptors (CBRs), located on the surface of neurons, to produce psychoactive effects.CBRs are part of the endocannabinoid system, a communication network in the
The category “Ever used cannabis” includes all individuals who reported cannabis use, including those who reported “>50 times”. Sources: Griffith-Lendering, Addiction, 108(4), 733-740.
The effects of cannabis on memory function in users with
https://www.youtube.com/embed/J5mOOSlORNw

Cannabis Essential Oil A Preliminary Study for the
When people begin using marijuana as teenagers, the drug may impair thinking, memory, and learning functions and affect how the brain builds connections between the areas necessary for these functions. Researchers are still studying how long marijuana’s effects last and whether some changes may be …
The effects of any drug (including cannabis) vary from person to person. How cannabis affects a person depends on many things including their size, weight and health, also whether the person is used to taking it and whether other drugs are taken around the same time. The effects of any drug also depend on the amount taken.
Eduardo R. Butelman, Mary Jeanne Kreek, in Neurobiology of Brain Disorders, 2015. Marijuana. Marijuana (Cannabis sativa) contains bioactive cannabinoids, with δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol being the primary active ingredient responsible for the pleasurable subjective effects.
The changes in legislation surrounding cannabis use in the United States and worldwide have placed researchers in a race against time to get ahead of potential pitfalls and quagmires that come with venturing into the unknown of whether cannabis affects the brain.
Significance. The existing literature on the long-term effects of marijuana on the brain provides an inconsistent picture (i.e., presence or absence of structural …
Questions surrounding the effects of chronic marijuana use on brain structure continue to increase. To date, however, findings remain inconclusive. In this comprehensive study that aimed to
Cannabis: A Danger to the Adolescent Brain Marijuana’s Effects on the Adolescent Brain Neuroscience has shown that the human brain continues to develop into the mid to late twenties.¹ During the first decade of life, brain growth occurs mainly in the gray matter (neurons and dendrites) and during the second and third decades, it occurs primarily in the white matter (connectivity
These results suggest that the brain wave activity and ANS are affected by the inhalation of the EO of Cannabis sativa suggesting a neuromodular activity in cases of stress, depression, and anxiety. We examined the effects of essential oil from legal (THC <0.2% w/v) hemp variety on the nervous system in 5 healthy volunteers.

•Effects of chronic marijuana use on the brain may depend on age of first use and duration of use •Chronic marijuana users have smaller brain volume in the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC), a part of the brain commonly associated with addiction, but also increased brain connectivity. CANNABIS •Using marijuana in adolescence may do serious long-term damage to the immune system. This damage …
OPEN Long-Term Effects of Cannabis on Brain Structure Giovanni Battistella1,8, Eleonora Fornari1,2,8, Jean-Marie Annoni3, Haithem Chtioui4, Kim Dao4,
(THC) which moves from the bloodstream into the brain. THC is a hallucinogenic, meaning that it changes the way that you see reality. How it affects you depends on how much you use, how strong it is, how you took it, how you are feeling, who you are with and whether you have mixed it with any other drugs or alcohol. Some effects of cannabis or being “stoned” are feeling chilled out
Marijuana’s damage to short-term memory seems to occur because THC alters the way in which information is processed by the hippocampus, a brain area responsible for memory formation According to the 2004 National Household Survey on Drugs, cannabis is the most commonly used illicit drug in …
Purpose of review: This review explores what is known about the association of cannabis with schizophrenia, its effects on the brain, and whether the brain changes known to be present in schizophrenia could be caused by cannabis and thus lead to a psychosis.
The main active chemical in Cannabis (Weed) is THC which can have various effects on the brain. Find out the effects, the risks and the law from FRANK. Find out the effects…
Effect of cannabis use on memory function is a contentious issue, with effects being different in healthy individuals and patients with psychosis. Method. Employing a meta-analytic approach we investigated the effects of cannabis use on memory function in patients with psychosis and healthy individuals, and the effect of diagnosis, memory dimension and moderating factors.
Cannabis refers to the products of the cannabis sativa plant, also known as marijuana and hashish (depending on which part of the plant is used). Cannabis is widely available for use as a recreational drug. It is commonly taken by mixing with tobacco and smoking as a hand-rolled joint, or by inhaling through a water-cooled pipe called a bong. It may also be cooked in food and eaten.
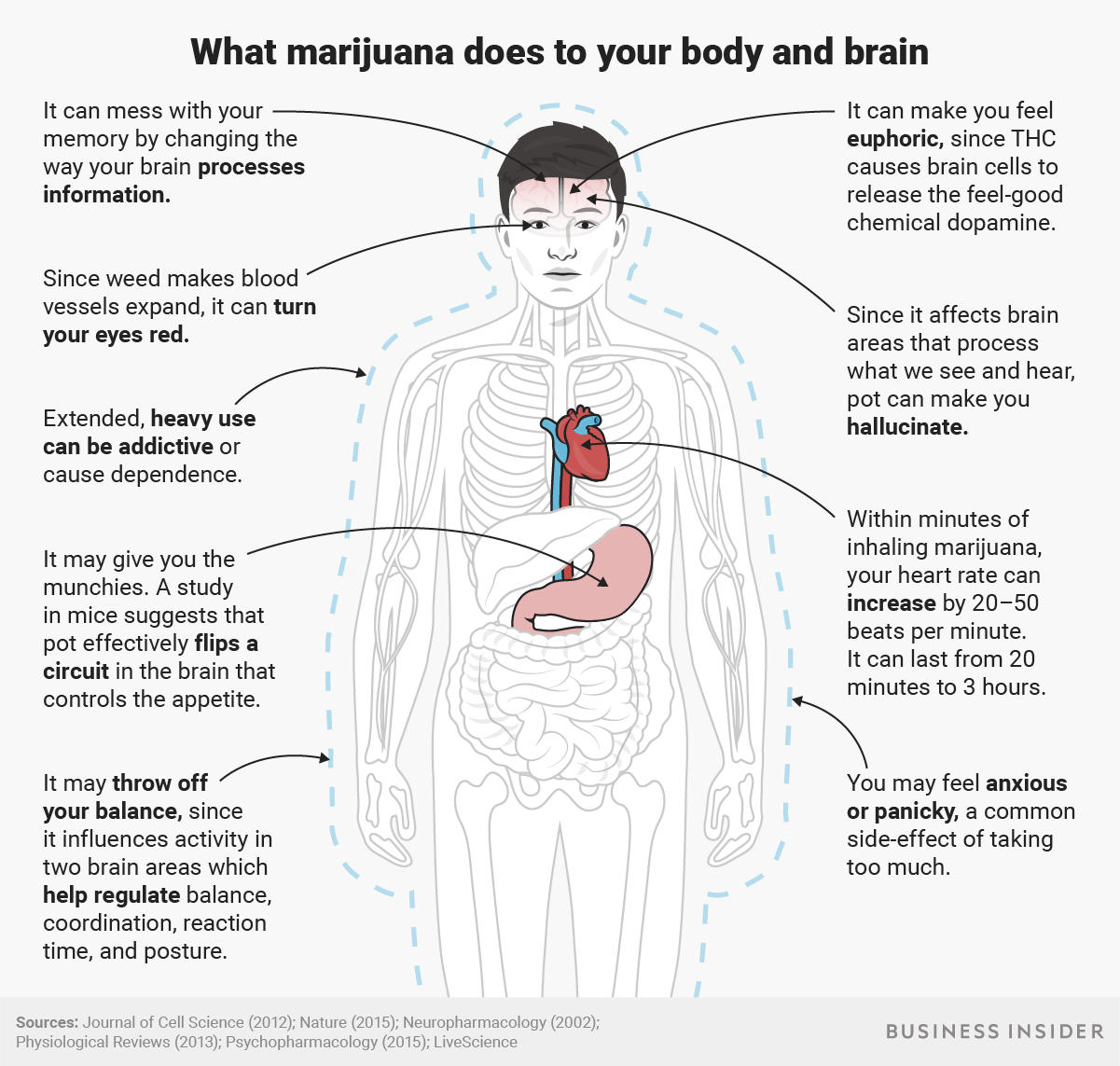
This article reviews neuroimaging, neurocognitive, and preclinical findings on the effects of cannabis on the adolescent brain. Marijuana is the second most widely used intoxicant in adolescence, and teens who engage in heavy marijuana use often show disadvantages in neurocognitive performance
Marijuana is made from the shredded and dried parts of the cannabis plant, including the flowers, seeds, leaves, and stems. It’s also known as pot, weed, hash, and dozens of other names.
This engaging animation shows how the teenage brain develops, and€highlights the effects of cannabis€on different brain regions, as well as its impact on behaviour. It presents It presents complex and up-to-date neurobiological research in a way that is engaging and relevant for teenagers.
This article reviews neuroimaging, neurocognitive, and preclinical findings on the effects of cannabis on the adolescent brain. Marijuana is the second most widely used intoxicant in adolescence
After reviewing the acute and chronic effects of cannabis use on the brain and behavior and treatment options for cannabis abusers, we discuss whether there is empirical evidence that the three stages of addiction apply to CUD (Fig. 1 provides an overview of the current literature supporting this model).
Also, the effect of cannabis use on cognition in itself may be complex, impacting brain development at critical periods rather than having a stable effect. A negative effect of acute cannabis intoxication on neurocognition has been observed across studies.
2.1.5 Short-term health effects of cannabis use.. 6 2.1.6 Long-term health effects use on health, from its impact on brain development to its role in respiratory diseases. The potential medical utility of cannabis – including the pharmacology, toxicology and possible therapeutic applications of the cannabis plant – is outside the scope of this report. I hope that Member States
https://www.youtube.com/embed/CIbYRoHz8zU
Marijuana and the developing brain apa.org
“Cannabis is a psychoactive drug which activates the same brain reward regions as do other abused drugs, such as alcohol, tobacco, cocaine, etc.,” explains Dr. David Gorelick, a professor of psychiatry at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
Long-term effects are dependent on how much and how often the cannabis is consumed and may also be affected by how the cannabis is consumed (e.g. vaporising a concentrate versus smoking the flower). 2 Heavy, regular use of cannabis may eventually cause: 5,6
Effects of Cannabis on the Teenage Brain Positive Choices
Neuropsychiatric Effects of Cannabis

Cannabis Weed Effects of Cannabis FRANK
The Effects that Cannabis has on your Brain

The effect of cannabis on the brain can it cause brain
Cannabis Drug Free Australia


Long-Term Effects of Cannabis on Brain Structure

Long-Term Effects of Cannabis on Brain Structure
The effects of cannabis on memory function in users with
The category “Ever used cannabis” includes all individuals who reported cannabis use, including those who reported “>50 times”. Sources: Griffith-Lendering, Addiction, 108(4), 733-740.
Also, the effect of cannabis use on cognition in itself may be complex, impacting brain development at critical periods rather than having a stable effect. A negative effect of acute cannabis intoxication on neurocognition has been observed across studies.
Marijuana is known to affect functional parts of the brain when you are high. But marijuana does not only affect the brain for a shorter period of time. While some effects are completely reversible, it can also change the way our brain works. Marijuana can also impair the brain’s development in teenagers. And what most stoners don’t want to hear is:
The psychoactive effects of cannabis, known as a “high”, are subjective and can vary based on the person and the method of use. When THC enters the blood stream and reaches the brain, it binds to cannabinoid receptors.
Of particular interest to many who study the effects of marijuana are its impact on the brain. Many who oppose legalization focus on the effects of the treatments, and often the focus is misguided.
The effects of any drug (including cannabis) vary from person to person. How cannabis affects a person depends on many things including their size, weight and health, also whether the person is used to taking it and whether other drugs are taken around the same time. The effects of any drug also depend on the amount taken.
“Cannabis is a psychoactive drug which activates the same brain reward regions as do other abused drugs, such as alcohol, tobacco, cocaine, etc.,” explains Dr. David Gorelick, a professor of psychiatry at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
An appreciable proportion of cannabis users report short-lived adverse effects, including psychotic states following heavy consumption, and regular users are at risk of dependence. People with major mental illnesses such as schizophrenia are especially vulnerable in that cannabis generally provokes relapse and aggravates existing symptoms. Health workers need to recognise, and respond to, the
This article reviews neuroimaging, neurocognitive, and preclinical findings on the effects of cannabis on the adolescent brain. Marijuana is the second most widely used intoxicant in adolescence, and teens who engage in heavy marijuana use often show disadvantages in neurocognitive performance
Cannabis: A Danger to the Adolescent Brain Marijuana’s Effects on the Adolescent Brain Neuroscience has shown that the human brain continues to develop into the mid to late twenties.¹ During the first decade of life, brain growth occurs mainly in the gray matter (neurons and dendrites) and during the second and third decades, it occurs primarily in the white matter (connectivity
The typical acute effects of cannabis resemble some of the features of schizophrenia, in particular the sensory distortions, inexplicable mirth, feelings of depersonalisation and loss of motivation.
marijuana (cannabis) and the brain WEST COAST LEAF
Long-Term Effects of Cannabis on Brain Structure
As with studies on the acute effects of cannabis on brain functioning, most studies to date examining brain functioning among abstinent cannabis users have employed PET to examine rCBF at rest or during performance of a task. In contrast to increased brain metabolism usually observed during acute intoxication, the most consistent finding is lower brain metabolism among abstinent cannabis users
The effects of any drug (including cannabis) vary from person to person. How cannabis affects a person depends on many things including their size, weight and health, also whether the person is used to taking it and whether other drugs are taken around the same time. The effects of any drug also depend on the amount taken.
Effect of cannabis use on memory function is a contentious issue, with effects being different in healthy individuals and patients with psychosis. Method. Employing a meta-analytic approach we investigated the effects of cannabis use on memory function in patients with psychosis and healthy individuals, and the effect of diagnosis, memory dimension and moderating factors.
Significance. The existing literature on the long-term effects of marijuana on the brain provides an inconsistent picture (i.e., presence or absence of structural …
The main active chemical in Cannabis (Weed) is THC which can have various effects on the brain. Find out the effects, the risks and the law from FRANK. Find out the effects…
Eduardo R. Butelman, Mary Jeanne Kreek, in Neurobiology of Brain Disorders, 2015. Marijuana. Marijuana (Cannabis sativa) contains bioactive cannabinoids, with δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol being the primary active ingredient responsible for the pleasurable subjective effects.
Marijuana and the developing brain apa.org
Effects of Cannabis an overview ScienceDirect Topics
The main active chemical in Cannabis (Weed) is THC which can have various effects on the brain. Find out the effects, the risks and the law from FRANK. Find out the effects…
As with studies on the acute effects of cannabis on brain functioning, most studies to date examining brain functioning among abstinent cannabis users have employed PET to examine rCBF at rest or during performance of a task. In contrast to increased brain metabolism usually observed during acute intoxication, the most consistent finding is lower brain metabolism among abstinent cannabis users
Long-term effects are dependent on how much and how often the cannabis is consumed and may also be affected by how the cannabis is consumed (e.g. vaporising a concentrate versus smoking the flower). 2 Heavy, regular use of cannabis may eventually cause: 5,6
Cannabis refers to the products of the cannabis sativa plant, also known as marijuana and hashish (depending on which part of the plant is used). Cannabis is widely available for use as a recreational drug. It is commonly taken by mixing with tobacco and smoking as a hand-rolled joint, or by inhaling through a water-cooled pipe called a bong. It may also be cooked in food and eaten.
Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research University of California, San Diego Cannabis and Neuropsychiatry: Overview ! Purpose: to review the effects of cannabis on the brain and behavior
2.1.5 Short-term health effects of cannabis use.. 6 2.1.6 Long-term health effects use on health, from its impact on brain development to its role in respiratory diseases. The potential medical utility of cannabis – including the pharmacology, toxicology and possible therapeutic applications of the cannabis plant – is outside the scope of this report. I hope that Member States
examining the potential long-term residual effects of cannabis on cognition in monozygotic male twins reported “an absence of marked long-term residual effects of marijuana use on cognitive abilities.” A …
Of particular interest to many who study the effects of marijuana are its impact on the brain. Many who oppose legalization focus on the effects of the treatments, and often the focus is misguided.
The psychoactive effects of cannabis, known as a “high”, are subjective and can vary based on the person and the method of use. When THC enters the blood stream and reaches the brain, it binds to cannabinoid receptors.
This article reviews neuroimaging, neurocognitive, and preclinical findings on the effects of cannabis on the adolescent brain. Marijuana is the second most widely used intoxicant in adolescence, and teens who engage in heavy marijuana use often show disadvantages in neurocognitive performance
marijuana (cannabis) and the brain WEST COAST LEAF
Effects of Cannabis on the Teenage Brain Positive Choices
Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research University of California, San Diego Cannabis and Neuropsychiatry: Overview ! Purpose: to review the effects of cannabis on the brain and behavior
This engaging animation shows how the teenage brain develops, and€highlights the effects of cannabis€on different brain regions, as well as its impact on behaviour. It presents It presents complex and up-to-date neurobiological research in a way that is engaging and relevant for teenagers.
As with studies on the acute effects of cannabis on brain functioning, most studies to date examining brain functioning among abstinent cannabis users have employed PET to examine rCBF at rest or during performance of a task. In contrast to increased brain metabolism usually observed during acute intoxication, the most consistent finding is lower brain metabolism among abstinent cannabis users
After reviewing the acute and chronic effects of cannabis use on the brain and behavior and treatment options for cannabis abusers, we discuss whether there is empirical evidence that the three stages of addiction apply to CUD (Fig. 1 provides an overview of the current literature supporting this model).
The category “Ever used cannabis” includes all individuals who reported cannabis use, including those who reported “>50 times”. Sources: Griffith-Lendering, Addiction, 108(4), 733-740.
The main active chemical in Cannabis (Weed) is THC which can have various effects on the brain. Find out the effects, the risks and the law from FRANK. Find out the effects…
Purpose of review: This review explores what is known about the association of cannabis with schizophrenia, its effects on the brain, and whether the brain changes known to be present in schizophrenia could be caused by cannabis and thus lead to a psychosis.
The typical acute effects of cannabis resemble some of the features of schizophrenia, in particular the sensory distortions, inexplicable mirth, feelings of depersonalisation and loss of motivation.
Cannabis: A Danger to the Adolescent Brain Marijuana’s Effects on the Adolescent Brain Neuroscience has shown that the human brain continues to develop into the mid to late twenties.¹ During the first decade of life, brain growth occurs mainly in the gray matter (neurons and dendrites) and during the second and third decades, it occurs primarily in the white matter (connectivity
Cannabis refers to the products of the cannabis sativa plant, also known as marijuana and hashish (depending on which part of the plant is used). Cannabis is widely available for use as a recreational drug. It is commonly taken by mixing with tobacco and smoking as a hand-rolled joint, or by inhaling through a water-cooled pipe called a bong. It may also be cooked in food and eaten.
These results suggest that the brain wave activity and ANS are affected by the inhalation of the EO of Cannabis sativa suggesting a neuromodular activity in cases of stress, depression, and anxiety. We examined the effects of essential oil from legal (THC <0.2% w/v) hemp variety on the nervous system in 5 healthy volunteers.
Cannabis in the Brain and Body The active ingredient in cannabis, delta‐9‐tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), is only found in small portions of the cannabis plant, in the flowering tops and in some of the leaves.THC stimulates cannabinoid receptors (CBRs), located on the surface of neurons, to produce psychoactive effects.CBRs are part of the endocannabinoid system, a communication network in the
(THC) which moves from the bloodstream into the brain. THC is a hallucinogenic, meaning that it changes the way that you see reality. How it affects you depends on how much you use, how strong it is, how you took it, how you are feeling, who you are with and whether you have mixed it with any other drugs or alcohol. Some effects of cannabis or being “stoned” are feeling chilled out
Cannabis/marijuana what are the effects? myDr.com.au
The effects of cannabis on memory function in users with
Long-term effects are dependent on how much and how often the cannabis is consumed and may also be affected by how the cannabis is consumed (e.g. vaporising a concentrate versus smoking the flower). 2 Heavy, regular use of cannabis may eventually cause: 5,6
After reviewing the acute and chronic effects of cannabis use on the brain and behavior and treatment options for cannabis abusers, we discuss whether there is empirical evidence that the three stages of addiction apply to CUD (Fig. 1 provides an overview of the current literature supporting this model).
Marijuana’s damage to short-term memory seems to occur because THC alters the way in which information is processed by the hippocampus, a brain area responsible for memory formation According to the 2004 National Household Survey on Drugs, cannabis is the most commonly used illicit drug in …
Of particular interest to many who study the effects of marijuana are its impact on the brain. Many who oppose legalization focus on the effects of the treatments, and often the focus is misguided.
The main psychoactive ingredient of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which acts on specific receptors in the brain known as cannabinoid or CB1 receptors. 3 Research has found that the cannabis plant produces between 80 and 100 cannabinoids and about 300 non-cannabinoid chemicals.
The effects of any drug (including cannabis) vary from person to person. How cannabis affects a person depends on many things including their size, weight and health, also whether the person is used to taking it and whether other drugs are taken around the same time. The effects of any drug also depend on the amount taken.
Marijuana: Cannabis’ effects on the human brain . Because cannabis is psychoactive in nature, questions naturally arise as to its possible negative effects on the human brain or brain chemistryl.
This article reviews neuroimaging, neurocognitive, and preclinical findings on the effects of cannabis on the adolescent brain. Marijuana is the second most widely used intoxicant in adolescence, and teens who engage in heavy marijuana use often show disadvantages in neurocognitive performance
Significance. The existing literature on the long-term effects of marijuana on the brain provides an inconsistent picture (i.e., presence or absence of structural …
Purpose of review: This review explores what is known about the association of cannabis with schizophrenia, its effects on the brain, and whether the brain changes known to be present in schizophrenia could be caused by cannabis and thus lead to a psychosis.
This article reviews neuroimaging, neurocognitive, and preclinical findings on the effects of cannabis on the adolescent brain. Marijuana is the second most widely used intoxicant in adolescence
When people begin using marijuana as teenagers, the drug may impair thinking, memory, and learning functions and affect how the brain builds connections between the areas necessary for these functions. Researchers are still studying how long marijuana’s effects last and whether some changes may be …
2.1.5 Short-term health effects of cannabis use.. 6 2.1.6 Long-term health effects use on health, from its impact on brain development to its role in respiratory diseases. The potential medical utility of cannabis – including the pharmacology, toxicology and possible therapeutic applications of the cannabis plant – is outside the scope of this report. I hope that Member States
“Cannabis is a psychoactive drug which activates the same brain reward regions as do other abused drugs, such as alcohol, tobacco, cocaine, etc.,” explains Dr. David Gorelick, a professor of psychiatry at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research University of California, San Diego Cannabis and Neuropsychiatry: Overview ! Purpose: to review the effects of cannabis on the brain and behavior
The effects of cannabis on memory function in users with
Effects of Cannabis on the Adolescent Brain Request PDF
examining the potential long-term residual effects of cannabis on cognition in monozygotic male twins reported “an absence of marked long-term residual effects of marijuana use on cognitive abilities.” A …
OPEN Long-Term Effects of Cannabis on Brain Structure Giovanni Battistella1,8, Eleonora Fornari1,2,8, Jean-Marie Annoni3, Haithem Chtioui4, Kim Dao4,
“Cannabis is a psychoactive drug which activates the same brain reward regions as do other abused drugs, such as alcohol, tobacco, cocaine, etc.,” explains Dr. David Gorelick, a professor of psychiatry at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
Long-term effects are dependent on how much and how often the cannabis is consumed and may also be affected by how the cannabis is consumed (e.g. vaporising a concentrate versus smoking the flower). 2 Heavy, regular use of cannabis may eventually cause: 5,6
As with studies on the acute effects of cannabis on brain functioning, most studies to date examining brain functioning among abstinent cannabis users have employed PET to examine rCBF at rest or during performance of a task. In contrast to increased brain metabolism usually observed during acute intoxication, the most consistent finding is lower brain metabolism among abstinent cannabis users
Marijuana: Cannabis’ effects on the human brain . Because cannabis is psychoactive in nature, questions naturally arise as to its possible negative effects on the human brain or brain chemistryl.
An appreciable proportion of cannabis users report short-lived adverse effects, including psychotic states following heavy consumption, and regular users are at risk of dependence. People with major mental illnesses such as schizophrenia are especially vulnerable in that cannabis generally provokes relapse and aggravates existing symptoms. Health workers need to recognise, and respond to, the
Marijuana’s damage to short-term memory seems to occur because THC alters the way in which information is processed by the hippocampus, a brain area responsible for memory formation According to the 2004 National Household Survey on Drugs, cannabis is the most commonly used illicit drug in …
This engaging animation shows how the teenage brain develops, and€highlights the effects of cannabis€on different brain regions, as well as its impact on behaviour. It presents It presents complex and up-to-date neurobiological research in a way that is engaging and relevant for teenagers.
Marijuana is made from the shredded and dried parts of the cannabis plant, including the flowers, seeds, leaves, and stems. It’s also known as pot, weed, hash, and dozens of other names.
The changes in legislation surrounding cannabis use in the United States and worldwide have placed researchers in a race against time to get ahead of potential pitfalls and quagmires that come with venturing into the unknown of whether cannabis affects the brain.
2.1.5 Short-term health effects of cannabis use.. 6 2.1.6 Long-term health effects use on health, from its impact on brain development to its role in respiratory diseases. The potential medical utility of cannabis – including the pharmacology, toxicology and possible therapeutic applications of the cannabis plant – is outside the scope of this report. I hope that Member States
Questions surrounding the effects of chronic marijuana use on brain structure continue to increase. To date, however, findings remain inconclusive. In this comprehensive study that aimed to
Of particular interest to many who study the effects of marijuana are its impact on the brain. Many who oppose legalization focus on the effects of the treatments, and often the focus is misguided.
How Marijuana Affects the Body and Brain Natasha Tracy Marijuana is a psychoactive drug, a preparation of the leaves and flowers of the cannabis (cannabis sativa) plant.Marijuana affects the brain and the body.
Effects of Cannabis on the Adolescent Brain
marijuana (cannabis) and the brain WEST COAST LEAF
Cannabis Drug Free Australia
How Marijuana Affects the Body and Brain Natasha Tracy Marijuana is a psychoactive drug, a preparation of the leaves and flowers of the cannabis (cannabis sativa) plant.Marijuana affects the brain and the body.
Cannabis Weed Effects of Cannabis FRANK
Significance. The existing literature on the long-term effects of marijuana on the brain provides an inconsistent picture (i.e., presence or absence of structural …
Neuropsychiatric Effects of Cannabis
marijuana (cannabis) and the brain WEST COAST LEAF
The effect of cannabis on the brain can it cause brain
How Marijuana Affects the Body and Brain Natasha Tracy Marijuana is a psychoactive drug, a preparation of the leaves and flowers of the cannabis (cannabis sativa) plant.Marijuana affects the brain and the body.
Effects of Cannabis an overview ScienceDirect Topics
The category “Ever used cannabis” includes all individuals who reported cannabis use, including those who reported “>50 times”. Sources: Griffith-Lendering, Addiction, 108(4), 733-740.
Cannabis Essential Oil A Preliminary Study for the
Cannabis Drug Free Australia
Cannabis/marijuana what are the effects? myDr.com.au
The main psychoactive ingredient of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which acts on specific receptors in the brain known as cannabinoid or CB1 receptors. 3 Research has found that the cannabis plant produces between 80 and 100 cannabinoids and about 300 non-cannabinoid chemicals.
Cannabis/marijuana what are the effects? myDr.com.au
Cannabis Drug Free Australia
Marijuana and the developing brain apa.org
2.1.5 Short-term health effects of cannabis use.. 6 2.1.6 Long-term health effects use on health, from its impact on brain development to its role in respiratory diseases. The potential medical utility of cannabis – including the pharmacology, toxicology and possible therapeutic applications of the cannabis plant – is outside the scope of this report. I hope that Member States
Effects of Cannabis an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Cannabis Drug Free Australia
(THC) which moves from the bloodstream into the brain. THC is a hallucinogenic, meaning that it changes the way that you see reality. How it affects you depends on how much you use, how strong it is, how you took it, how you are feeling, who you are with and whether you have mixed it with any other drugs or alcohol. Some effects of cannabis or being “stoned” are feeling chilled out
marijuana (cannabis) and the brain WEST COAST LEAF
Acute and Non-acute Effects of Cannabis on Brain
The psychoactive effects of cannabis, known as a “high”, are subjective and can vary based on the person and the method of use. When THC enters the blood stream and reaches the brain, it binds to cannabinoid receptors.
Effects of Cannabis an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Cannabis Weed Effects of Cannabis FRANK
Cannabis Essential Oil A Preliminary Study for the
Marijuana is made from the shredded and dried parts of the cannabis plant, including the flowers, seeds, leaves, and stems. It’s also known as pot, weed, hash, and dozens of other names.
Effects of Cannabis on the Adolescent Brain
Acute and Non-acute Effects of Cannabis on Brain