Chemical properties of monosaccharides pdf
texture, but also for their chemical and nutritional properties [4,5]. Nowadays, edible mushrooms have Nowadays, edible mushrooms have become an attractive functional food mainly due to their chemical composition of polysaccharides.
Chemical Properties Core Drive Results Phase 2 Phase 1
Monosaccharide, also called simple sugar, any of the basic compounds that serve as the building blocks of carbohydrates. Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones ; that is, they are molecules with more than one hydroxyl group (―OH), and a carbonyl group (C=O) either at the terminal carbon atom (aldose) or at the second carbon atom (ketose).
There is more than one molecule with the molecular formula C 5 H 10 O 5 and more than one with the molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6. Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae are called structural isomers.
Chemical Properties of Monosaccharides Like D-glucose, all monosaccharides with at least five carbons exist predominately in the cyclic form. Six member rings are called pyranose rings Five member rings are called furanose rings . 12 Conformations of Monosaccharides Conformations of β-D-ribofuranose Conformations of β-D-glucopyranose Haworth projection Chair conformation Boat …
Sucrose is ubiquitous in food preparations due to both its sweetness and its functional properties; it is important to the structure of many foods including biscuits and cookies, ice cream and sorbets, and also assists in the preservation of foods. As such it is common in many processed and so-called junk foods.
Polysaccharide: Polysaccharide, the form in which most natural carbohydrates occur. Polysaccharides may have a molecular structure that is either branched or linear. Linear compounds such as cellulose often pack together to form a rigid structure; branched forms (e.g., gum arabic) generally are …
Compare and contrast monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, • Carbohydrates are a large class of naturally occurring polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. • Monosaccharides (also known as simple sugars) are the simplest carbohydrates containing 3-7 carbon atoms. A sugar containing: – an aldehyde is known as an aldose – a ketone is known as a ketose . Classification of
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and may be subcategorized as aldoses or ketoses. The sugar is an aldose if it contains an aldehyde functional group. A ketose signifies that the sugar contains a ketone functional group. Monosaccharides may be further classified based on the
Chemical Properties of Carbohydrates Monosaccharides are the simplest units of carbohydrates and the simplest form of sugar. They are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates such as
Chemical Methods The monosaccharides have aldehyde or keto functional groups which have powerful reducing properties by virtue of their ability to form enediol arrangements. These form the basis of a series of reductiometric procedures which are widely used.
The chemical bond between two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond. Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide that consists of a bond between one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose. Maltose is a disaccharide that consists of two glucose molecules. Lactose (milk sugar) is another disaccharide and it is created by a bond between one molecule of galactose and one …
Horton Chapter 8 College of Charleston
https://www.youtube.com/embed/aJl8XjKbaVo

Chemical composition and molecular structure of
Acyclic monosaccharides have three different characteristics: the number of carbon atoms it contains, its D or L configuration, and the placement of its carbonyl group (aldehyde or ketone). These characteristics are combined to name monosaccharide carbohydrates.
The chemical bond between two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond. Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide that consists of a bond between …
In fact, the functional properties of polysaccharide plant gums are governed by the chemical composition, molecular weight, sequence of monosaccharide, configuration of glycoside linkages, and the position of glycoside linkages in the backbone and side chains .
Monosaccharides are a single unit of sugar Mono=Single unit Saccharide= sugar They are simple sugars such as fructose glucose . They are a source of energy for some living beings.

Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. GALACTOSE Galactose (from Greek γάλακτος galaktos “milk”), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is less sweet than glucose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose. Galactan is a polymer of the …
chemical properties of the sulfamate proton in solution. The singlet peak observed for GlcNS happens due to fast chemical exchange of the GlcNS sulfamate proton in solution. Analyses on kinetics of alpha-beta anomeric mutarotation via 1H NMR spectra have been performed in GlcNS as well as other glucose-based monosaccharides. 1D 1H and 2D 1H-15N HSQC spectra recorded at low temperature …
Video: Chemical Properties of Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide energy for cells to do work. This lesson will discuss what different carbohydrates are made of and what their purpose is. The
The resulting polymers and block copolymers exhibit sugar-responsive solubilization in aqueous buffer solutions (pH = 7.4−7.8) in the presence of monosaccharides such as d-fructose and d-glucose. Polymeric Monosaccharide Receptors Responsive at Neutral pH – Journal of the American Chemical Society (ACS Publications)
Examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and glyceraldehyde. Polysaccharides, meanwhile, have a general formula of C x (H 2 O) y where x is usually a large number between 200 and 2500. When the repeating units in the polymer backbone are six-carbon monosaccharides, as is often the case, the general formula simplifies to (C 6 H 10 O 5 ) n , where typically 40≤n≤3000.
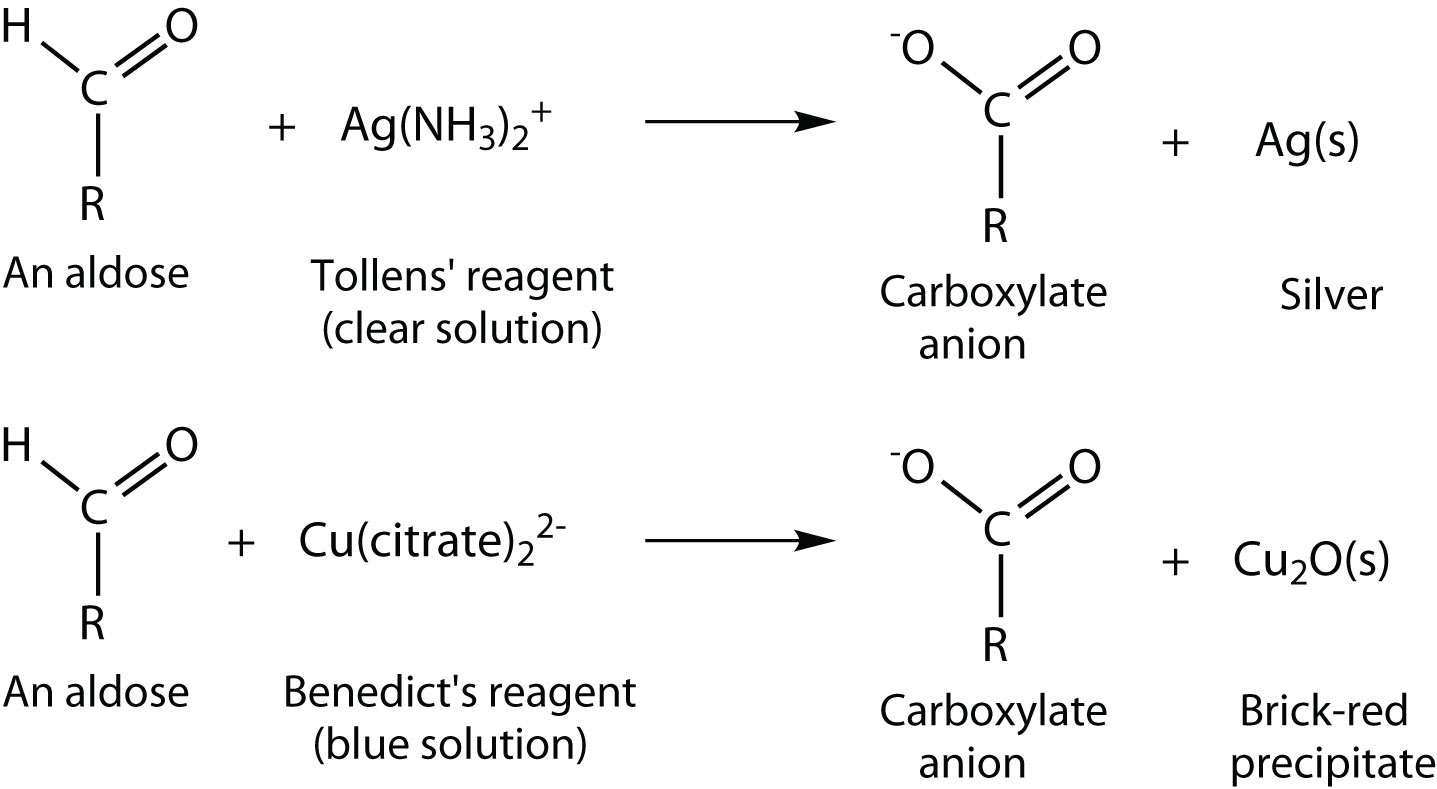
The chemical behavior of these monosaccharides is likewise determined by their functional groups. An important reaction of monosaccharides is the oxidation of the aldehyde group, one of the most easily oxidized organic functional groups.
Three common monosaccharides are sucrose, lactose and maltose. “Disaccharide” is one of the four chemical groupings of carbohydrates (monosaccharide, …
Disaccharides, or chemical formula of C n (H 2 O) n-1, n > 5, are namely two monosaccharides linked by condensation or dehydration synthesis. As a result, a glycosidic bond is formed when the -OH of one sugar molecule joins with that of another sugar molecule.
Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Rye Nonstarch Polysaccharides. I. Colorimetric Analysis of Pentosans and Their Relative Monosaccharide Compositions in Fractionated (Milled) …
Discuss the structural, chemical, and biochemical properties of the three common disaccharides. A. Describe the nature of the glycosidic bond(s) in the common disaccharides. B. Identify the disaccharide as reducing or non reducing.
The configuration of the monosaccharides Journal of
new century maths 9 answers pdf
Polysaccharide chemical compound Britannica.com
1H and 15N NMR Analyses on Heparin Heparan Sulfates and

Chemical Characteristics and Antioxidant Properties of
https://www.youtube.com/embed/fUKUwADHZt8
What are the chemical properties of monosaccharides? Quora



principles of naval architecture pdf

https://www.youtube.com/embed/ijKHT948H40
7 Q&As to Study the Properties of Carbohydrates
What are the chemical properties of monosaccharides? Quora
The chemical bond between two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond. Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide that consists of a bond between one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose. Maltose is a disaccharide that consists of two glucose molecules. Lactose (milk sugar) is another disaccharide and it is created by a bond between one molecule of galactose and one …
Monosaccharide, also called simple sugar, any of the basic compounds that serve as the building blocks of carbohydrates. Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones ; that is, they are molecules with more than one hydroxyl group (―OH), and a carbonyl group (C=O) either at the terminal carbon atom (aldose) or at the second carbon atom (ketose).
Polysaccharide: Polysaccharide, the form in which most natural carbohydrates occur. Polysaccharides may have a molecular structure that is either branched or linear. Linear compounds such as cellulose often pack together to form a rigid structure; branched forms (e.g., gum arabic) generally are …
Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. GALACTOSE Galactose (from Greek γάλακτος galaktos “milk”), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is less sweet than glucose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose. Galactan is a polymer of the …
texture, but also for their chemical and nutritional properties [4,5]. Nowadays, edible mushrooms have Nowadays, edible mushrooms have become an attractive functional food mainly due to their chemical composition of polysaccharides.
Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Rye Nonstarch Polysaccharides. I. Colorimetric Analysis of Pentosans and Their Relative Monosaccharide Compositions in Fractionated (Milled) …
Chemical Properties Core Drive Results Phase 2 Phase 1
Acyclic monosaccharides have three different characteristics: the number of carbon atoms it contains, its D or L configuration, and the placement of its carbonyl group (aldehyde or ketone). These characteristics are combined to name monosaccharide carbohydrates.
Chemical Properties of Monosaccharides Like D-glucose, all monosaccharides with at least five carbons exist predominately in the cyclic form. Six member rings are called pyranose rings Five member rings are called furanose rings . 12 Conformations of Monosaccharides Conformations of β-D-ribofuranose Conformations of β-D-glucopyranose Haworth projection Chair conformation Boat …
Chemical Methods The monosaccharides have aldehyde or keto functional groups which have powerful reducing properties by virtue of their ability to form enediol arrangements. These form the basis of a series of reductiometric procedures which are widely used.
1H and 15N NMR Analyses on Heparin Heparan Sulfates and
What are the chemical properties of monosaccharides? Quora
Chemical Properties of Monosaccharides Like D-glucose, all monosaccharides with at least five carbons exist predominately in the cyclic form. Six member rings are called pyranose rings Five member rings are called furanose rings . 12 Conformations of Monosaccharides Conformations of β-D-ribofuranose Conformations of β-D-glucopyranose Haworth projection Chair conformation Boat …
Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Rye Nonstarch Polysaccharides. I. Colorimetric Analysis of Pentosans and Their Relative Monosaccharide Compositions in Fractionated (Milled) …
Chemical Methods The monosaccharides have aldehyde or keto functional groups which have powerful reducing properties by virtue of their ability to form enediol arrangements. These form the basis of a series of reductiometric procedures which are widely used.
The chemical bond between two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond. Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide that consists of a bond between one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose. Maltose is a disaccharide that consists of two glucose molecules. Lactose (milk sugar) is another disaccharide and it is created by a bond between one molecule of galactose and one …
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and may be subcategorized as aldoses or ketoses. The sugar is an aldose if it contains an aldehyde functional group. A ketose signifies that the sugar contains a ketone functional group. Monosaccharides may be further classified based on the
Chemical Properties of Carbohydrates Monosaccharides are the simplest units of carbohydrates and the simplest form of sugar. They are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates such as
There is more than one molecule with the molecular formula C 5 H 10 O 5 and more than one with the molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6. Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae are called structural isomers.
Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. GALACTOSE Galactose (from Greek γάλακτος galaktos “milk”), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is less sweet than glucose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose. Galactan is a polymer of the …
Video: Chemical Properties of Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide energy for cells to do work. This lesson will discuss what different carbohydrates are made of and what their purpose is. The
Chemical Characteristics and Antioxidant Properties of
Chemical composition and molecular structure of
Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. GALACTOSE Galactose (from Greek γάλακτος galaktos “milk”), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is less sweet than glucose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose. Galactan is a polymer of the …
Discuss the structural, chemical, and biochemical properties of the three common disaccharides. A. Describe the nature of the glycosidic bond(s) in the common disaccharides. B. Identify the disaccharide as reducing or non reducing.
Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Rye Nonstarch Polysaccharides. I. Colorimetric Analysis of Pentosans and Their Relative Monosaccharide Compositions in Fractionated (Milled) …
Chemical Properties of Monosaccharides Like D-glucose, all monosaccharides with at least five carbons exist predominately in the cyclic form. Six member rings are called pyranose rings Five member rings are called furanose rings . 12 Conformations of Monosaccharides Conformations of β-D-ribofuranose Conformations of β-D-glucopyranose Haworth projection Chair conformation Boat …
Compare and contrast monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, • Carbohydrates are a large class of naturally occurring polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. • Monosaccharides (also known as simple sugars) are the simplest carbohydrates containing 3-7 carbon atoms. A sugar containing: – an aldehyde is known as an aldose – a ketone is known as a ketose . Classification of
Sucrose is ubiquitous in food preparations due to both its sweetness and its functional properties; it is important to the structure of many foods including biscuits and cookies, ice cream and sorbets, and also assists in the preservation of foods. As such it is common in many processed and so-called junk foods.
Video: Chemical Properties of Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide energy for cells to do work. This lesson will discuss what different carbohydrates are made of and what their purpose is. The
In fact, the functional properties of polysaccharide plant gums are governed by the chemical composition, molecular weight, sequence of monosaccharide, configuration of glycoside linkages, and the position of glycoside linkages in the backbone and side chains .
Polysaccharide: Polysaccharide, the form in which most natural carbohydrates occur. Polysaccharides may have a molecular structure that is either branched or linear. Linear compounds such as cellulose often pack together to form a rigid structure; branched forms (e.g., gum arabic) generally are …
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and may be subcategorized as aldoses or ketoses. The sugar is an aldose if it contains an aldehyde functional group. A ketose signifies that the sugar contains a ketone functional group. Monosaccharides may be further classified based on the
Monosaccharide, also called simple sugar, any of the basic compounds that serve as the building blocks of carbohydrates. Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones ; that is, they are molecules with more than one hydroxyl group (―OH), and a carbonyl group (C=O) either at the terminal carbon atom (aldose) or at the second carbon atom (ketose).
The resulting polymers and block copolymers exhibit sugar-responsive solubilization in aqueous buffer solutions (pH = 7.4−7.8) in the presence of monosaccharides such as d-fructose and d-glucose. Polymeric Monosaccharide Receptors Responsive at Neutral pH – Journal of the American Chemical Society (ACS Publications)
chemical properties of the sulfamate proton in solution. The singlet peak observed for GlcNS happens due to fast chemical exchange of the GlcNS sulfamate proton in solution. Analyses on kinetics of alpha-beta anomeric mutarotation via 1H NMR spectra have been performed in GlcNS as well as other glucose-based monosaccharides. 1D 1H and 2D 1H-15N HSQC spectra recorded at low temperature …
1H and 15N NMR Analyses on Heparin Heparan Sulfates and
Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Rye
The chemical bond between two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond. Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide that consists of a bond between …
Discuss the structural, chemical, and biochemical properties of the three common disaccharides. A. Describe the nature of the glycosidic bond(s) in the common disaccharides. B. Identify the disaccharide as reducing or non reducing.
Chemical Properties of Carbohydrates Monosaccharides are the simplest units of carbohydrates and the simplest form of sugar. They are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates such as
Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. GALACTOSE Galactose (from Greek γάλακτος galaktos “milk”), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is less sweet than glucose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose. Galactan is a polymer of the …
Chemical Properties Core Drive Results Phase 2 Phase 1
Monosaccharides are a single unit of sugar Mono=Single unit Saccharide= sugar They are simple sugars such as fructose glucose . They are a source of energy for some living beings.
Chemical Properties of Monosaccharides Like D-glucose, all monosaccharides with at least five carbons exist predominately in the cyclic form. Six member rings are called pyranose rings Five member rings are called furanose rings . 12 Conformations of Monosaccharides Conformations of β-D-ribofuranose Conformations of β-D-glucopyranose Haworth projection Chair conformation Boat …
Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Rye Nonstarch Polysaccharides. I. Colorimetric Analysis of Pentosans and Their Relative Monosaccharide Compositions in Fractionated (Milled) …
The resulting polymers and block copolymers exhibit sugar-responsive solubilization in aqueous buffer solutions (pH = 7.4−7.8) in the presence of monosaccharides such as d-fructose and d-glucose. Polymeric Monosaccharide Receptors Responsive at Neutral pH – Journal of the American Chemical Society (ACS Publications)
texture, but also for their chemical and nutritional properties [4,5]. Nowadays, edible mushrooms have Nowadays, edible mushrooms have become an attractive functional food mainly due to their chemical composition of polysaccharides.
The chemical bond between two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond. Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide that consists of a bond between one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose. Maltose is a disaccharide that consists of two glucose molecules. Lactose (milk sugar) is another disaccharide and it is created by a bond between one molecule of galactose and one …
Acyclic monosaccharides have three different characteristics: the number of carbon atoms it contains, its D or L configuration, and the placement of its carbonyl group (aldehyde or ketone). These characteristics are combined to name monosaccharide carbohydrates.
Three common monosaccharides are sucrose, lactose and maltose. “Disaccharide” is one of the four chemical groupings of carbohydrates (monosaccharide, …
Video: Chemical Properties of Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide energy for cells to do work. This lesson will discuss what different carbohydrates are made of and what their purpose is. The
Sucrose is ubiquitous in food preparations due to both its sweetness and its functional properties; it is important to the structure of many foods including biscuits and cookies, ice cream and sorbets, and also assists in the preservation of foods. As such it is common in many processed and so-called junk foods.
Chemical composition and molecular structure of
The configuration of the monosaccharides Journal of
Three common monosaccharides are sucrose, lactose and maltose. “Disaccharide” is one of the four chemical groupings of carbohydrates (monosaccharide, …
Chemical Properties Core Drive Results Phase 2 Phase 1
Acyclic monosaccharides have three different characteristics: the number of carbon atoms it contains, its D or L configuration, and the placement of its carbonyl group (aldehyde or ketone). These characteristics are combined to name monosaccharide carbohydrates.
Chemical Methods The monosaccharides have aldehyde or keto functional groups which have powerful reducing properties by virtue of their ability to form enediol arrangements. These form the basis of a series of reductiometric procedures which are widely used.
The chemical bond between two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond. Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide that consists of a bond between …
texture, but also for their chemical and nutritional properties [4,5]. Nowadays, edible mushrooms have Nowadays, edible mushrooms have become an attractive functional food mainly due to their chemical composition of polysaccharides.
Discuss the structural, chemical, and biochemical properties of the three common disaccharides. A. Describe the nature of the glycosidic bond(s) in the common disaccharides. B. Identify the disaccharide as reducing or non reducing.
Chemical Properties of Monosaccharides Like D-glucose, all monosaccharides with at least five carbons exist predominately in the cyclic form. Six member rings are called pyranose rings Five member rings are called furanose rings . 12 Conformations of Monosaccharides Conformations of β-D-ribofuranose Conformations of β-D-glucopyranose Haworth projection Chair conformation Boat …
Chemical Properties of Carbohydrates Monosaccharides are the simplest units of carbohydrates and the simplest form of sugar. They are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates such as
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and may be subcategorized as aldoses or ketoses. The sugar is an aldose if it contains an aldehyde functional group. A ketose signifies that the sugar contains a ketone functional group. Monosaccharides may be further classified based on the
Video: Chemical Properties of Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide energy for cells to do work. This lesson will discuss what different carbohydrates are made of and what their purpose is. The
Disaccharides, or chemical formula of C n (H 2 O) n-1, n > 5, are namely two monosaccharides linked by condensation or dehydration synthesis. As a result, a glycosidic bond is formed when the -OH of one sugar molecule joins with that of another sugar molecule.
There is more than one molecule with the molecular formula C 5 H 10 O 5 and more than one with the molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6. Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae are called structural isomers.
The chemical bond between two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond. Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide that consists of a bond between one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose. Maltose is a disaccharide that consists of two glucose molecules. Lactose (milk sugar) is another disaccharide and it is created by a bond between one molecule of galactose and one …
Three common monosaccharides are sucrose, lactose and maltose. “Disaccharide” is one of the four chemical groupings of carbohydrates (monosaccharide, …
The configuration of the monosaccharides Journal of
Monosaccharides are a single unit of sugar Mono=Single unit Saccharide= sugar They are simple sugars such as fructose glucose . They are a source of energy for some living beings.
Chemical Properties of Monosaccharides prezi.com
Compare and contrast monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, • Carbohydrates are a large class of naturally occurring polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. • Monosaccharides (also known as simple sugars) are the simplest carbohydrates containing 3-7 carbon atoms. A sugar containing: – an aldehyde is known as an aldose – a ketone is known as a ketose . Classification of
Horton Chapter 8 College of Charleston
Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Rye
Disaccharides, or chemical formula of C n (H 2 O) n-1, n > 5, are namely two monosaccharides linked by condensation or dehydration synthesis. As a result, a glycosidic bond is formed when the -OH of one sugar molecule joins with that of another sugar molecule.
What are the chemical properties of monosaccharides? Quora
Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Rye
Polysaccharide chemical compound Britannica.com
Sucrose is ubiquitous in food preparations due to both its sweetness and its functional properties; it is important to the structure of many foods including biscuits and cookies, ice cream and sorbets, and also assists in the preservation of foods. As such it is common in many processed and so-called junk foods.
Polysaccharide chemical compound Britannica.com
Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Rye
Horton Chapter 8 College of Charleston
Polysaccharide: Polysaccharide, the form in which most natural carbohydrates occur. Polysaccharides may have a molecular structure that is either branched or linear. Linear compounds such as cellulose often pack together to form a rigid structure; branched forms (e.g., gum arabic) generally are …
The configuration of the monosaccharides Journal of
Polysaccharide chemical compound Britannica.com